Table of Contents
- 1. Electricity management and RCP
Plan electricity management
- 1. Electricity management and RCP
This article describes the installation planning. For on-site implementation and equipment configuration on the Climkit platform, refer to the links at the end of the article.
1. Electricity management and RCP
The Climkit electricity management solution consists of providing meters to measure and read electricity consumption, transmitting data to the platform, and activating one of the available operating methods, such as generating individual statements or automatic consumer billing.
The solution is generally applied within the framework of a self-consumption community (RCP).
It can also be used in other contexts, for example:
- In a commercial building to distinguish consumption between different surface areas
- In a campsite or port to account for consumption by pitch
- In any situation requiring the measurement, accounting, and billing of electricity consumption
Standard connection diagram for an RCP
There are several connection modes for electricity meters and communication depending on the number of consumers and buildings on a site.
The standard scheme consists of an RCP with:
- A single point of introduction to the grid with a DSO input meter
- Several consumers (apartments, offices, common areas, etc.) connected to private meters.
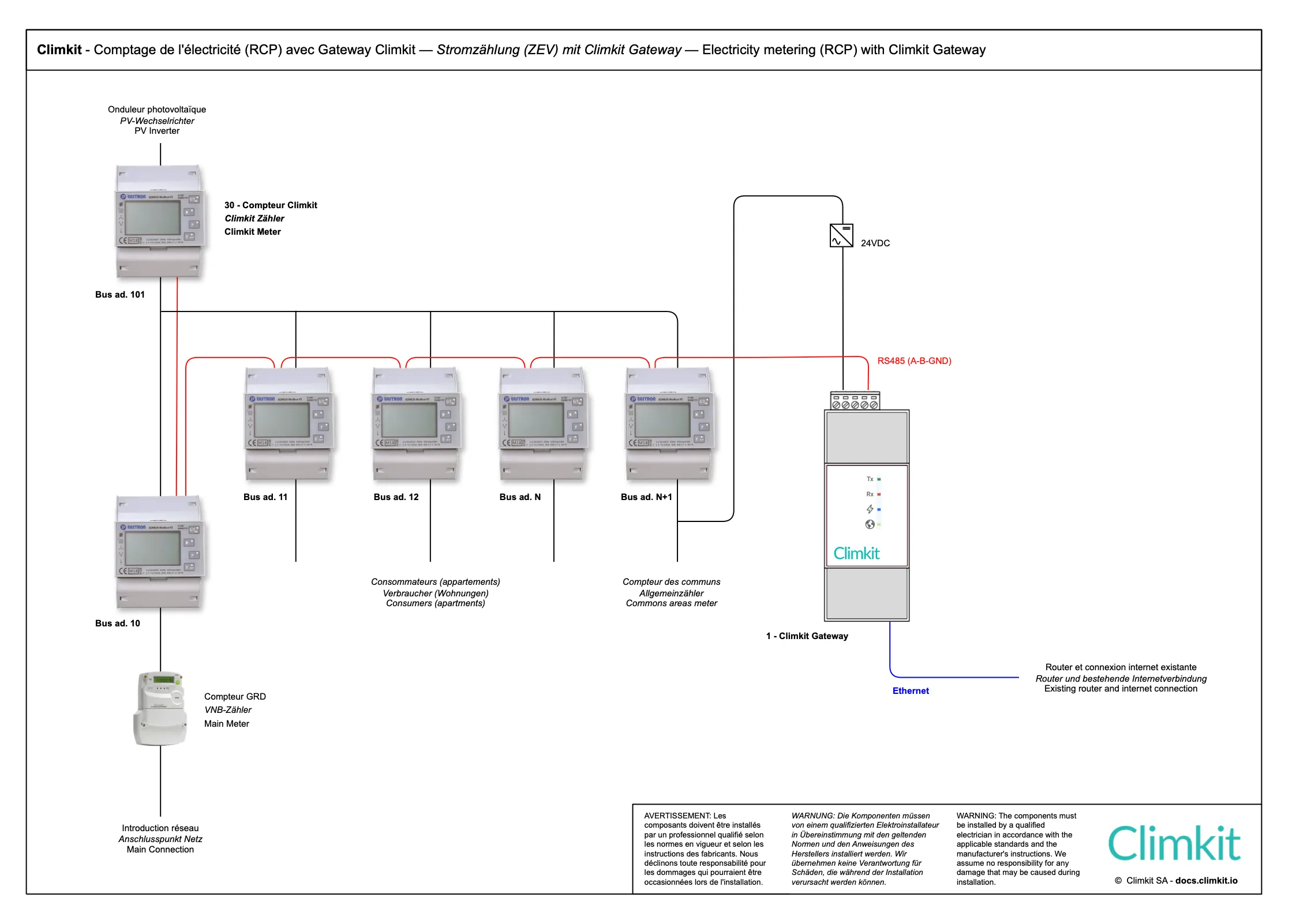
Electrical connection
The diagram above shows the case of an RCP with a single DSO meter at the electrical introduction of the building.
Consumers such as apartments and common areas are measured by private meters.
A private meter also measures photovoltaic production (inverter output).
A private meter is also installed at the introduction in series with the DSO one.
The number of meters depends on what needs to be measured and billed separately. Here is a list of the most common meters to consider:
- Heat pump: to distinguish its consumption from the rest of the common areas
- Charging stations for electric vehicles
- Battery connected in AC (and not in DC via a hybrid inverter)
- Photovoltaic inverters: one meter per installation allows measuring their performance separately and detecting potential problems more easily.

RS485 communication bus and internet connection
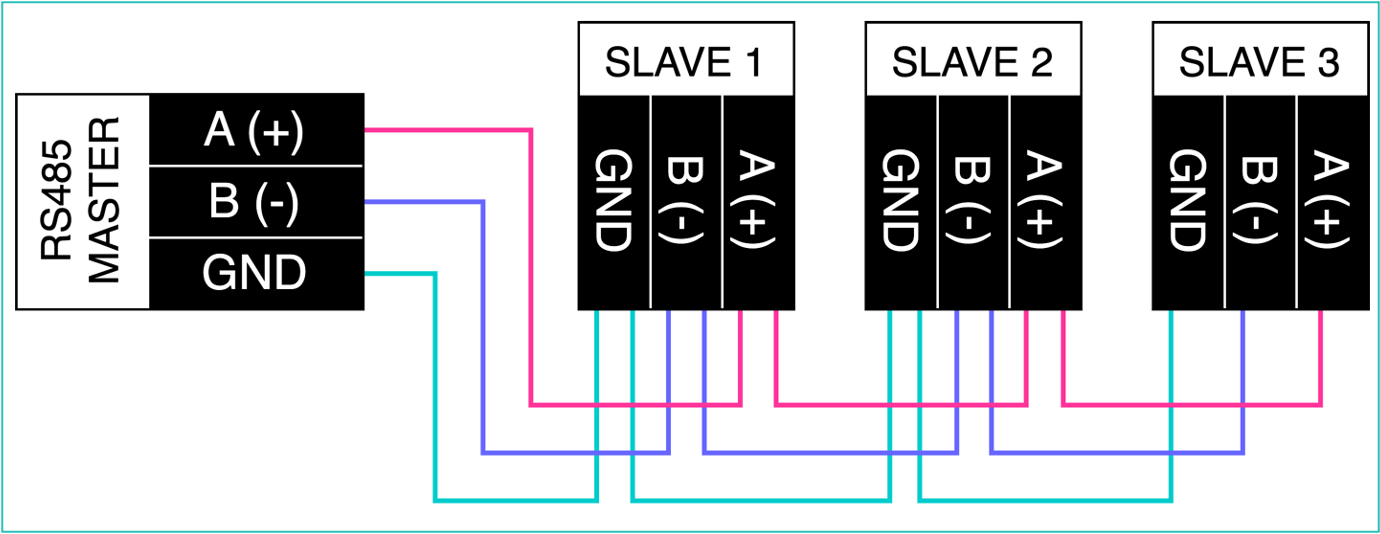
A serial communication bus of type RS485 connects each meter to the RS485 interface of the Climkit Gateway.
The meters (Slaves) are connected by an RS485 bus network to the Gateway (Master) according to the diagram below.
Directives and recommendations for cable pulling:
- Use a shielded U72 type cable (aluminum foil type) 4 × 0.8 mm².
- All devices must be connected in series (daisy-chain). Avoid branches, stars, or T-connections which can generate communication failures.
- The cable must not form closed loops.
- Maximum length: aim for < 500 m for a safety margin.
- Avoid passing near equipment that could create interference (motors, drives...).
The Gateway is itself connected via its Ethernet interface to the 4G Router equipped with a multi-operator SIM card to allow remote meter reading.


Climkit offer
The standard Climkit offer bundles the necessary elements for system operation: hardware equipment, software features, as well as services related to the setup.
All hardware is provided preconfigured to simplify installation and ensure proper communication of the meters.
- Equipment:
- LAN router or 4G Router
- Climkit Gateway
- Electricity meters
- Software features:
- Reading and visualization of electricity meters
- Setup service:
- Technical coordination and meter reading verification
- Administrative setup
All products are ordered directly from Climkit.
In most cases, installation can be performed by the installer without an on-site intervention by a Climkit technician.
Telephone assistance is available if necessary during commissioning.
Details of equipment used
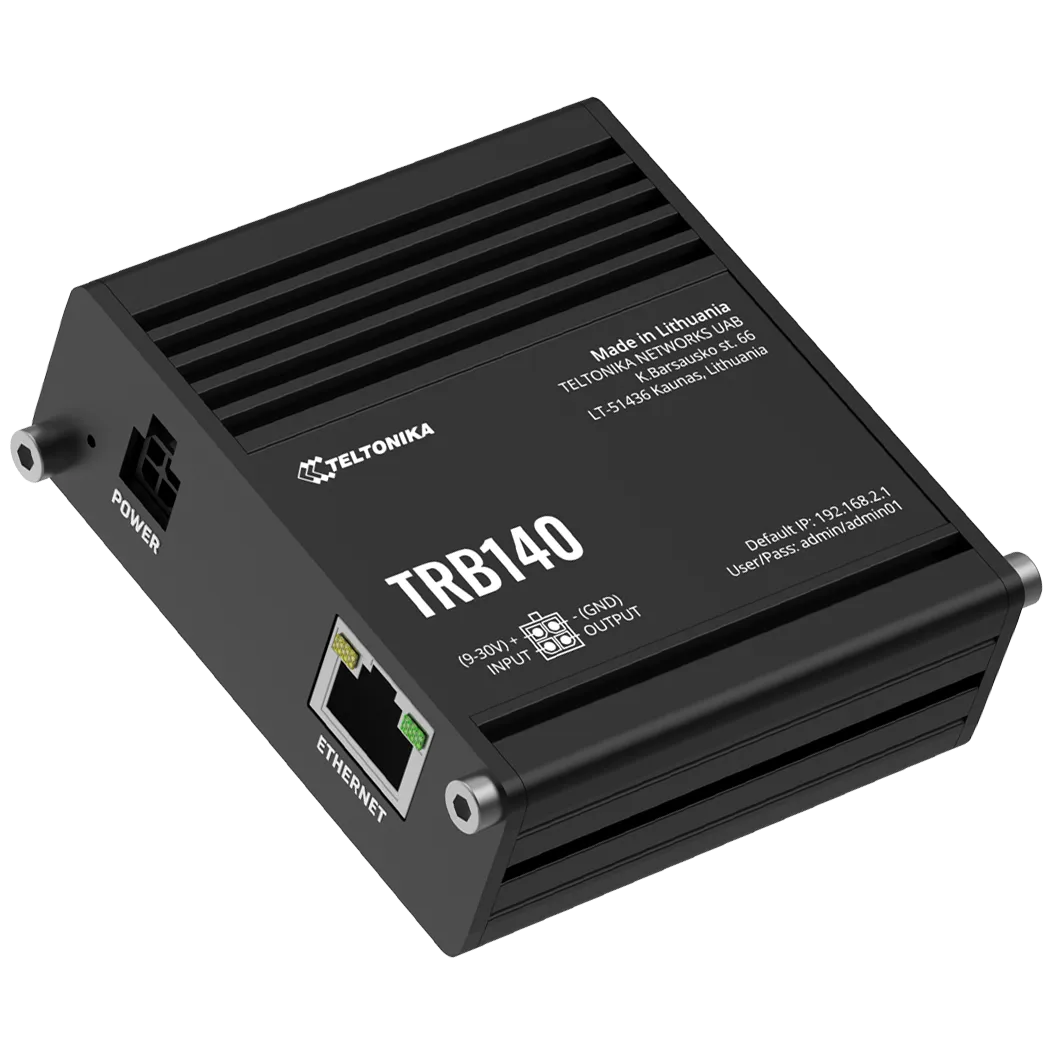
4G Router
An internet connection is essential for system operation. If no connection is available, Climkit can provide it via a 4G Router equipped with an active multi-operator SIM card.
Using the Climkit TRB140 4G Router offers several advantages:
- Simplified installation: the router is easily installed inside the electrical cabinet, directly on the DIN rail
- Complete delivery: supplied with its DIN rail support and its 24V DC power supply
- Ready to use: delivered preconfigured with an activated SIM card
- Economical 4G subscription: low-cost internet connection

Climkit Gateway
The Climkit Gateway reads meters connected to its RS485 port via the Modbus protocol and transmits readings to the Climkit platform via the internet.

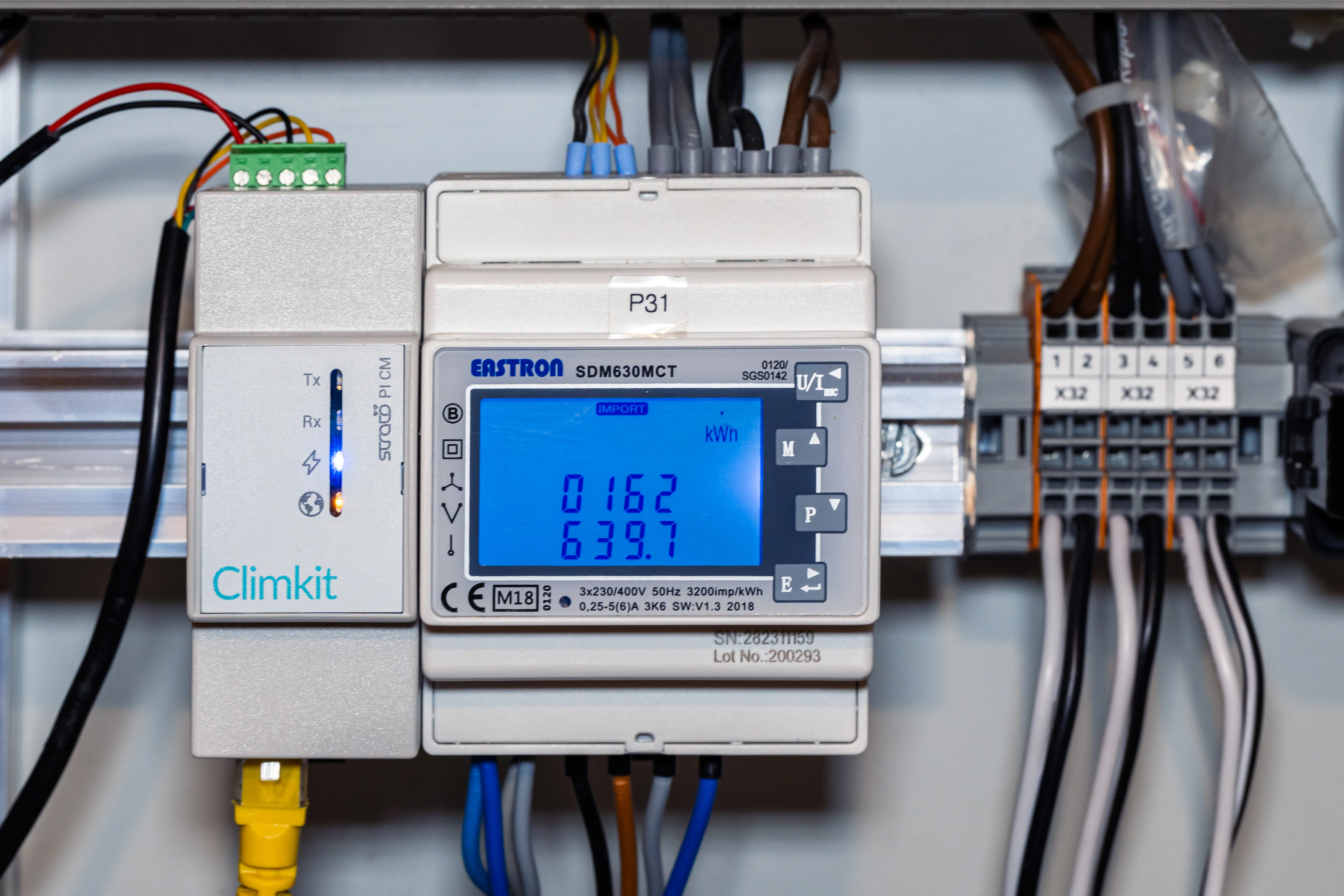
Electricity meters
Electricity meters allow measuring consumption, production as well as imported energy and energy fed back to the grid.
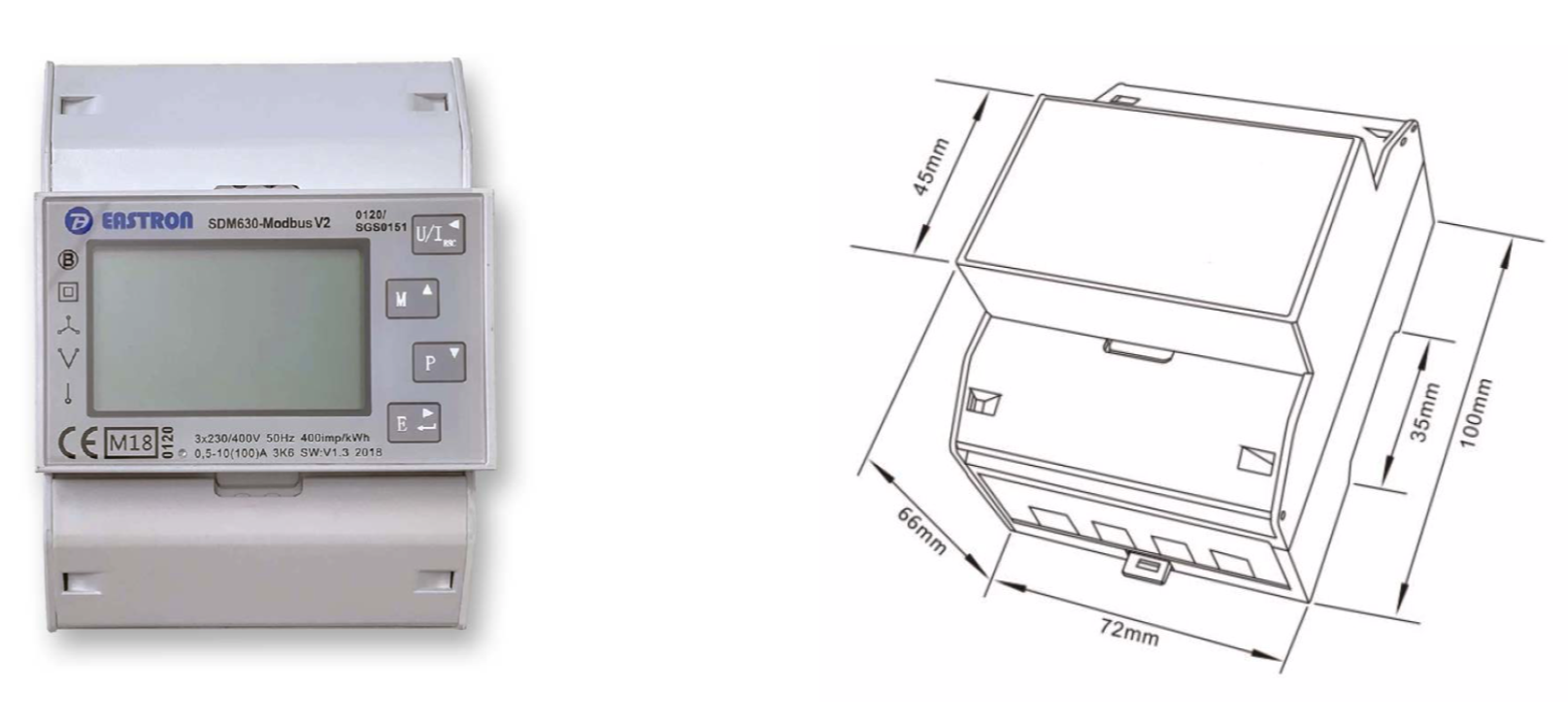
In the case of a connection below 80A, Climkit provides direct electricity meters, meaning the conductor wires pass directly through the meter.
The model generally provided is the Eastron SDM630Modbus meter. The meter is 4 DIN modules wide and installs directly in the electrical cabinet on a DIN rail or in a suitable box (see T-Box below).

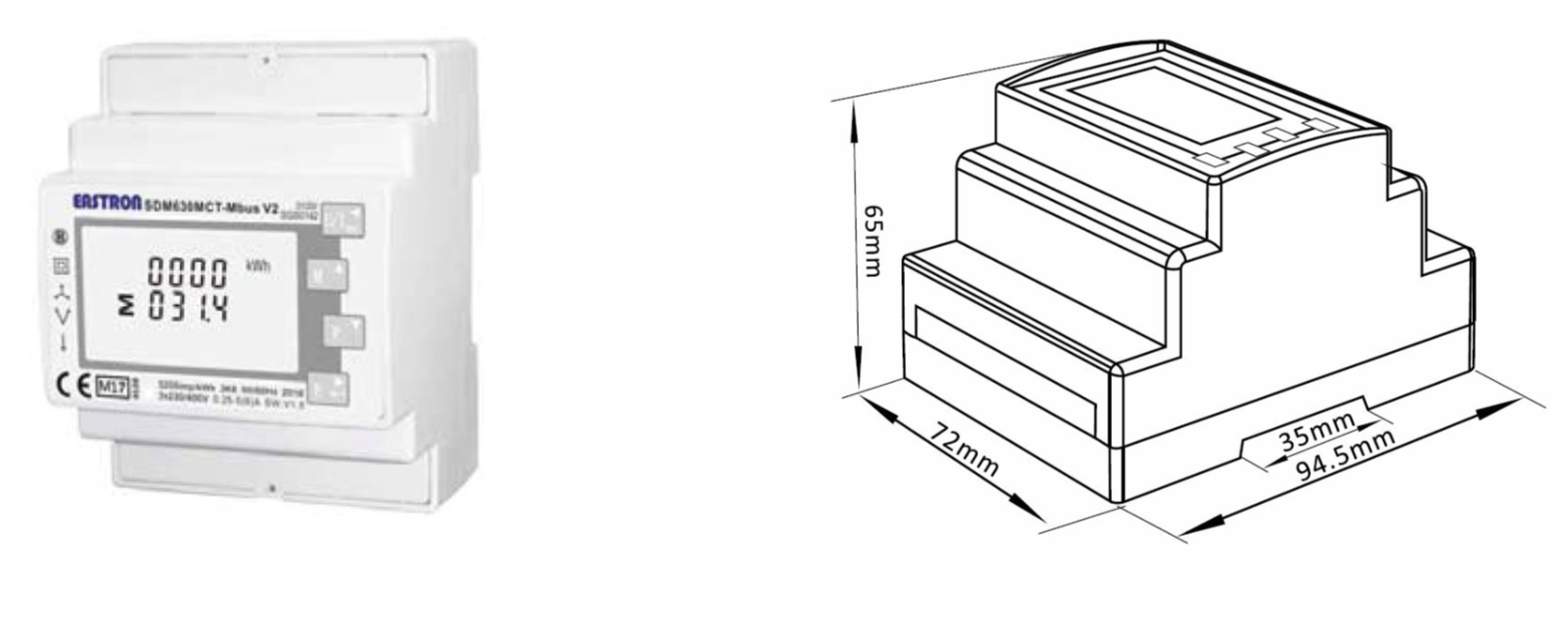
In cases where the connection intensity (amperage) exceeds 80A, Climkit provides indirect electricity meters, meaning the conductor wires pass through current transformers (CT) which are themselves connected to the meter.
- The model generally provided is the Eastron SDM630MCT meter

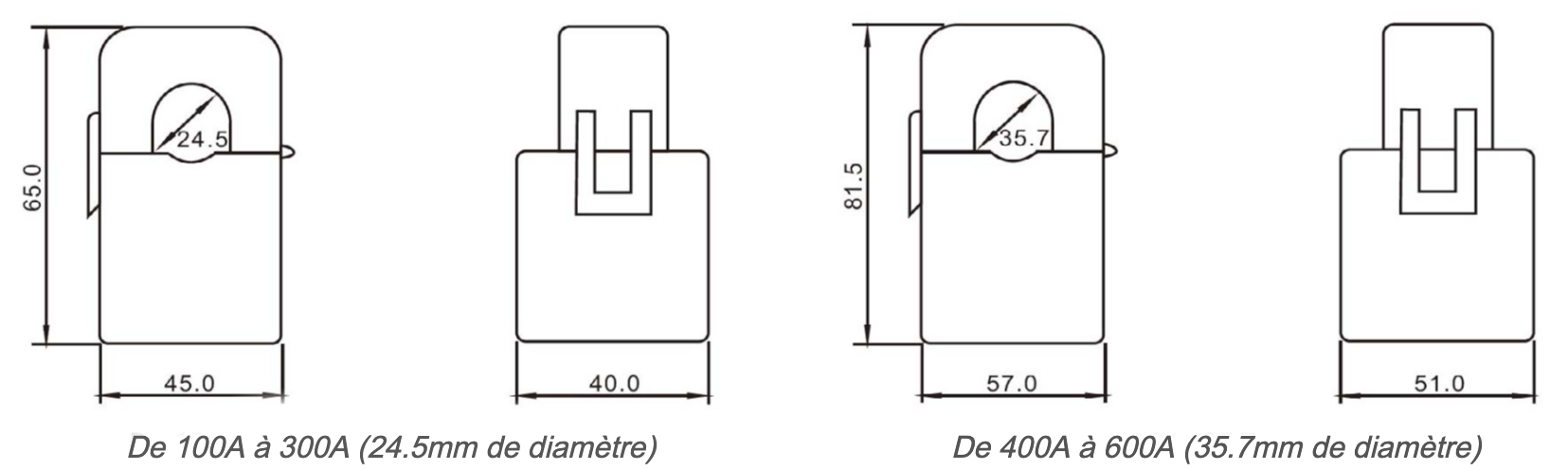
Current Transformers (CT)
CTs are chosen according to the connection intensity and the diameter of the conductor onto which the CT will clip around.
Climkit provides CTs ranging from 100 A to 2000 A.
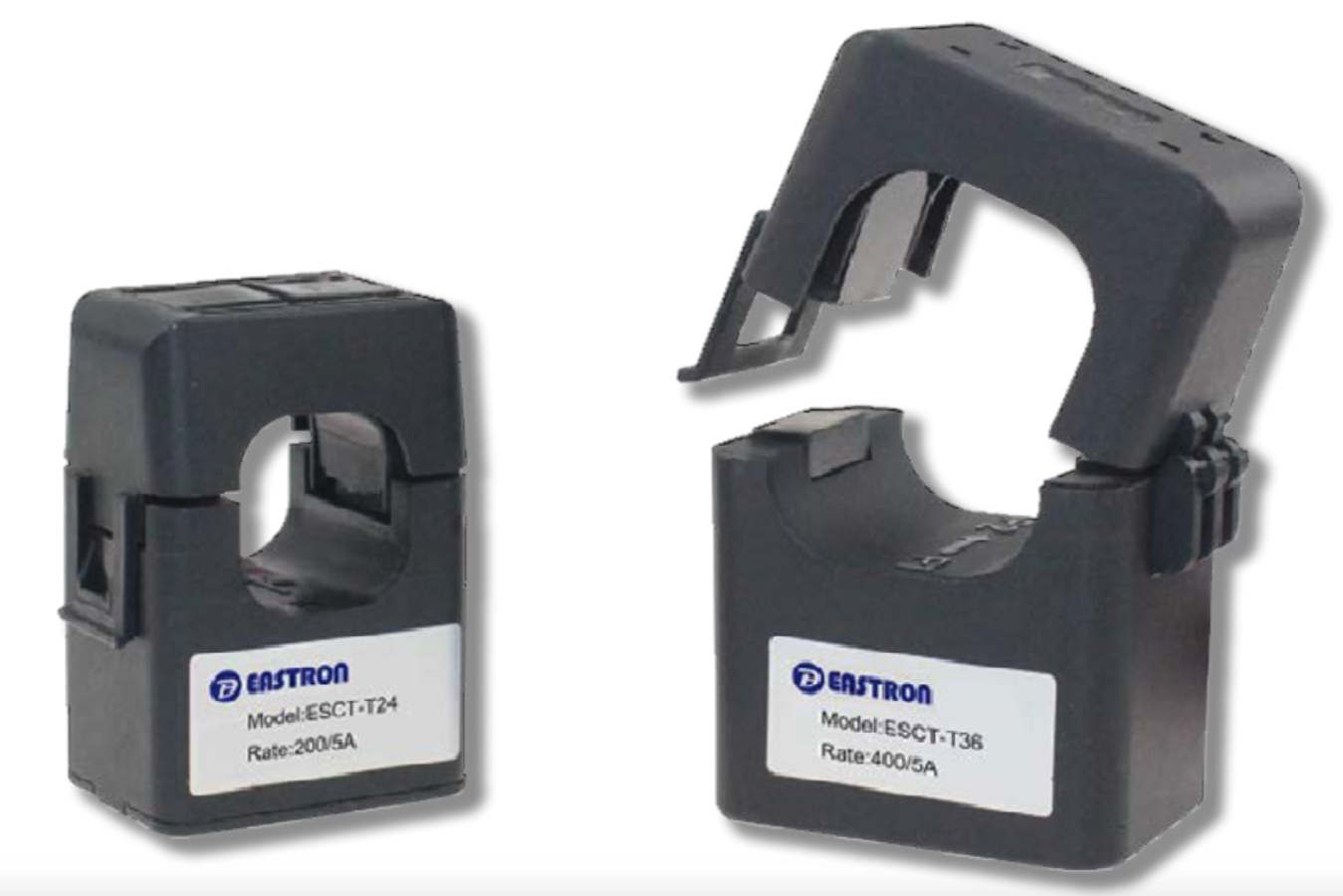
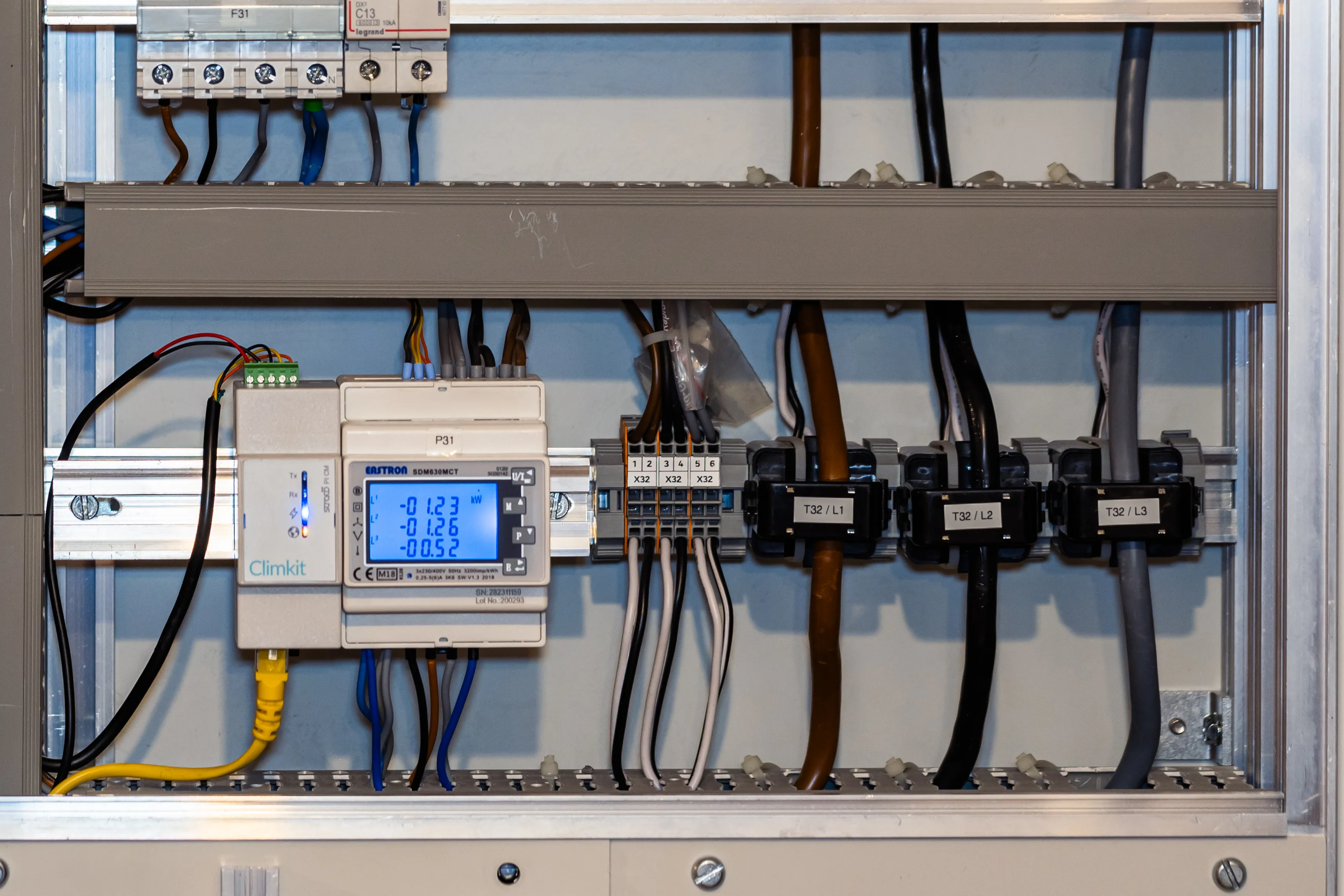


The CTs clip directly onto the cable or copper bar of each phase. Pay attention to the cable section relative to the CT diameter.
Other CTs can be ordered for specific cases with a larger diameter. To be specified at the time of order.
T-Box enclosure and meter plate
To facilitate meter installation on DSO meter locations, it is possible to order DIN rail enclosures with a mounting plate.

DIN rail enclosure on T-mounting plate (H: 36cm, W: 21cm)
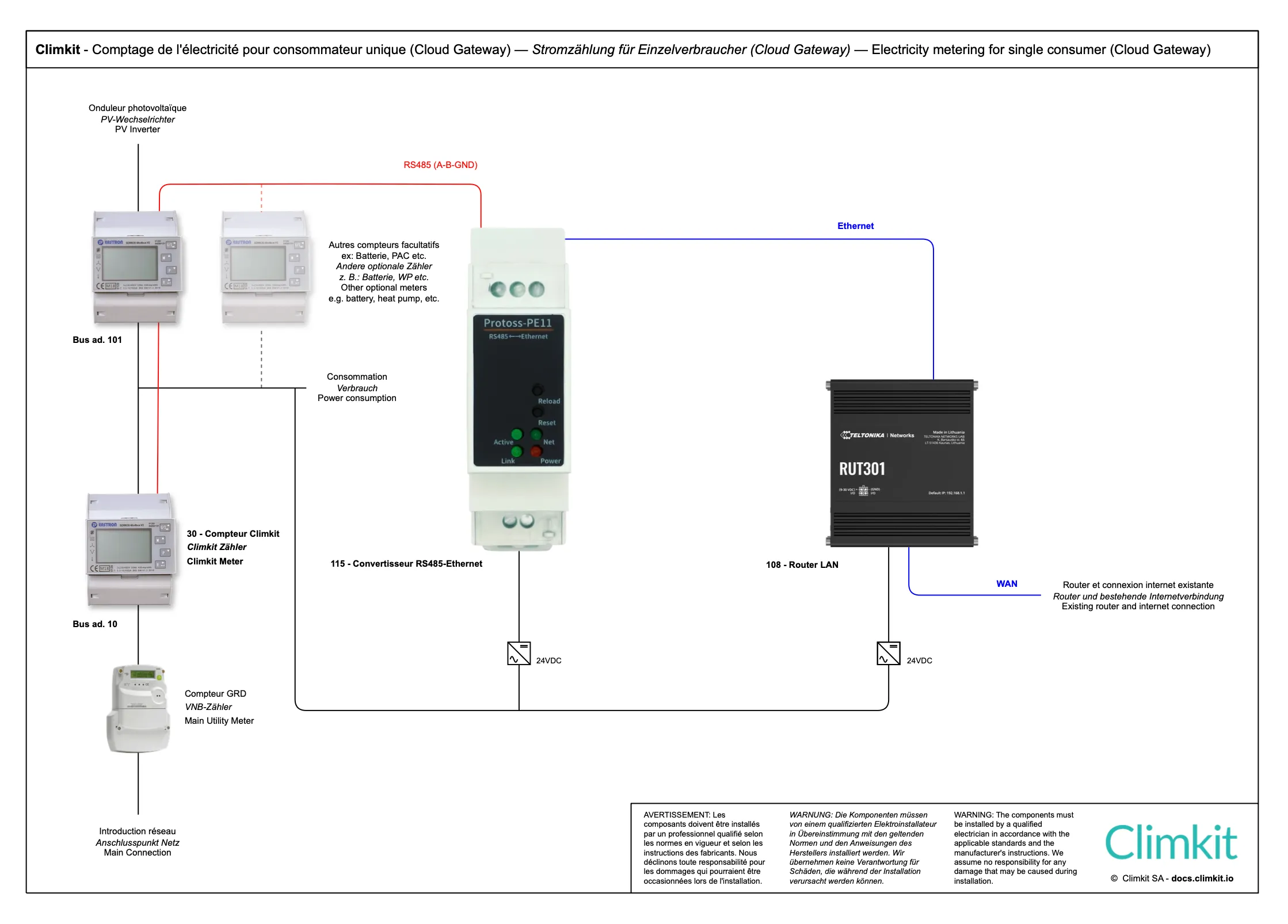
Variant with Cloud Gateway
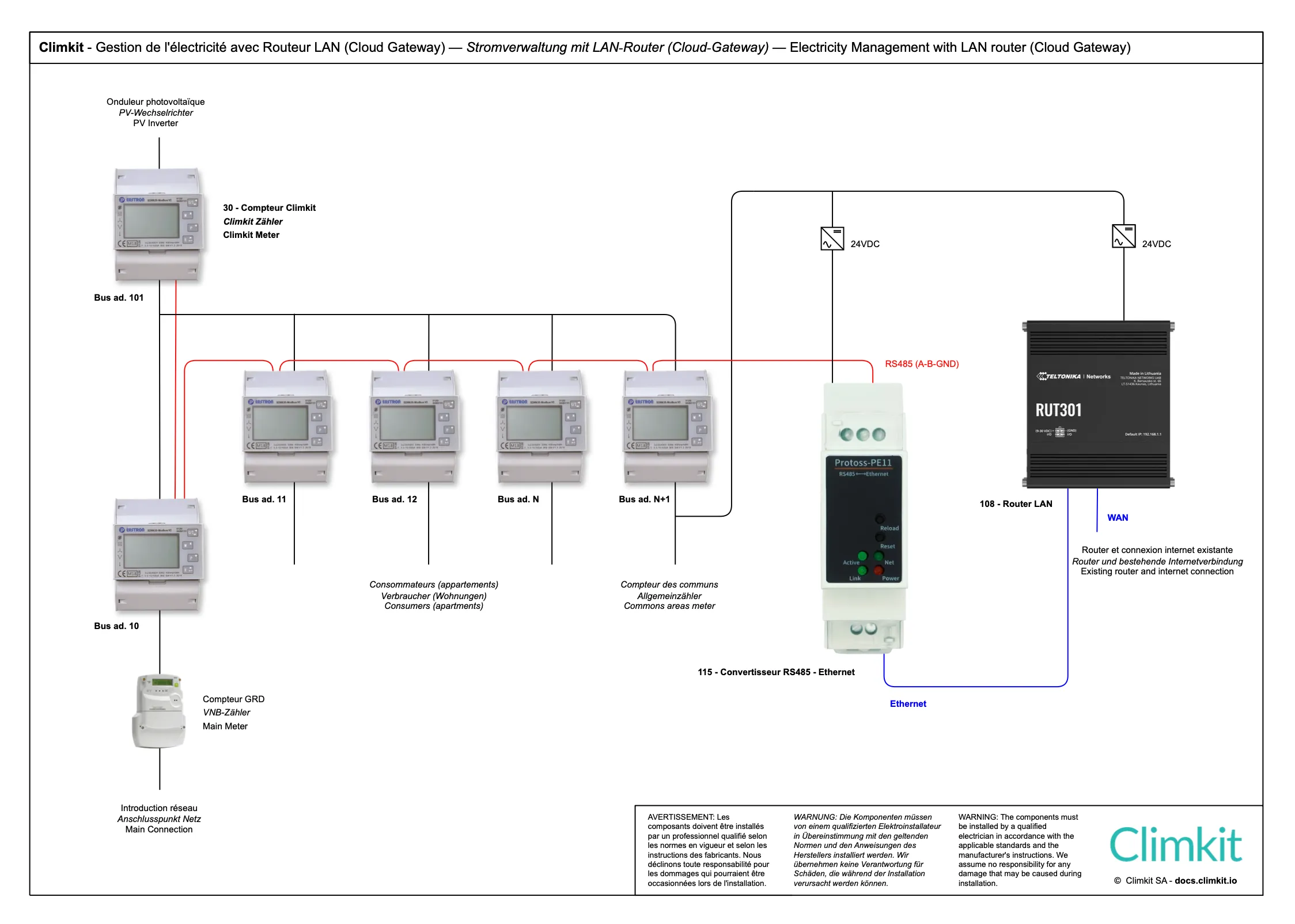
Instead of using a Climkit Gateway, it is possible to opt for a virtual Gateway using the MQTT protocol, by combining a router (LAN or 4G) with an RS485-Ethernet converter.
Cloud Gateway diagram with 4G Router
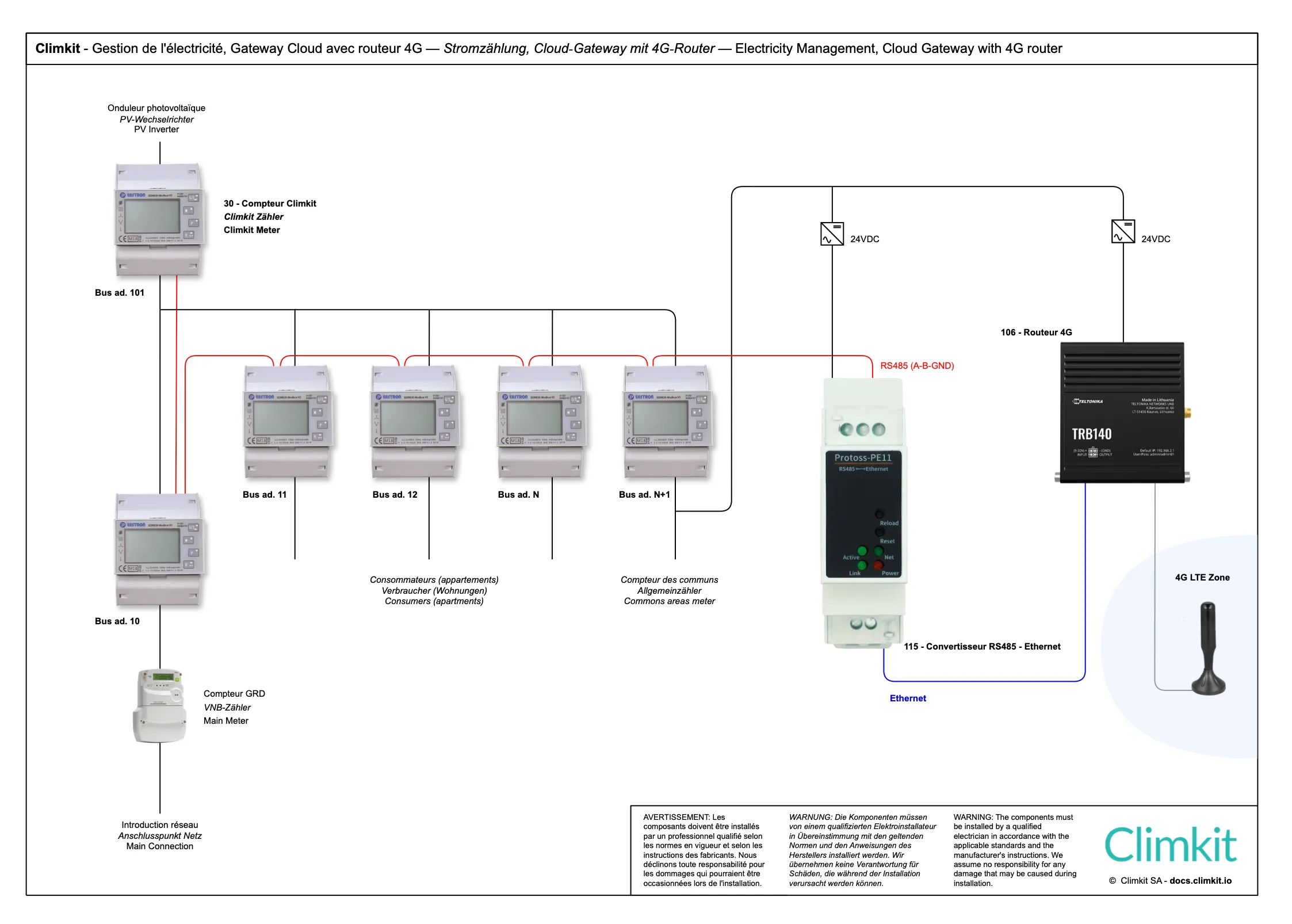
Diagram with LAN router
2. Connection variants
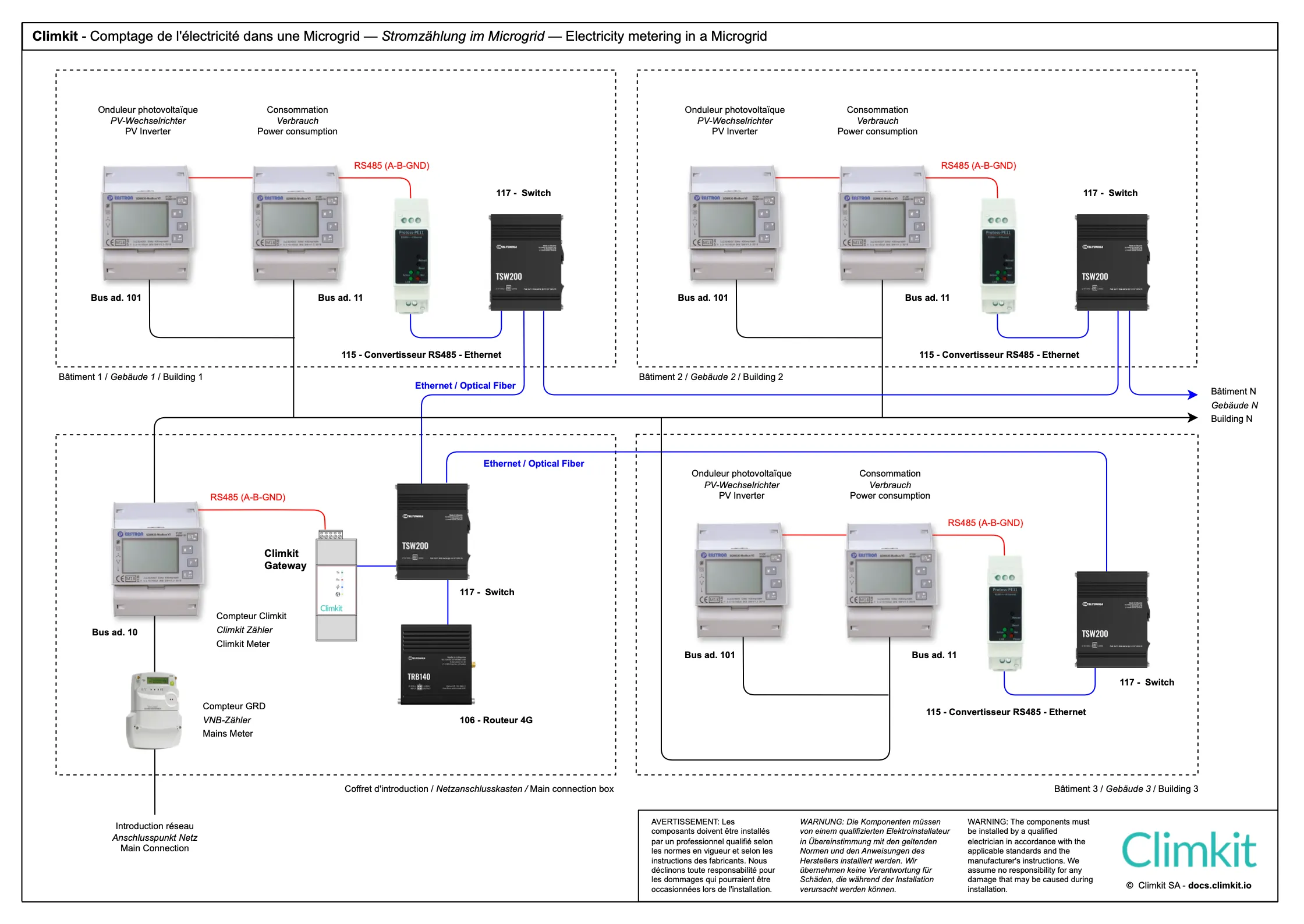
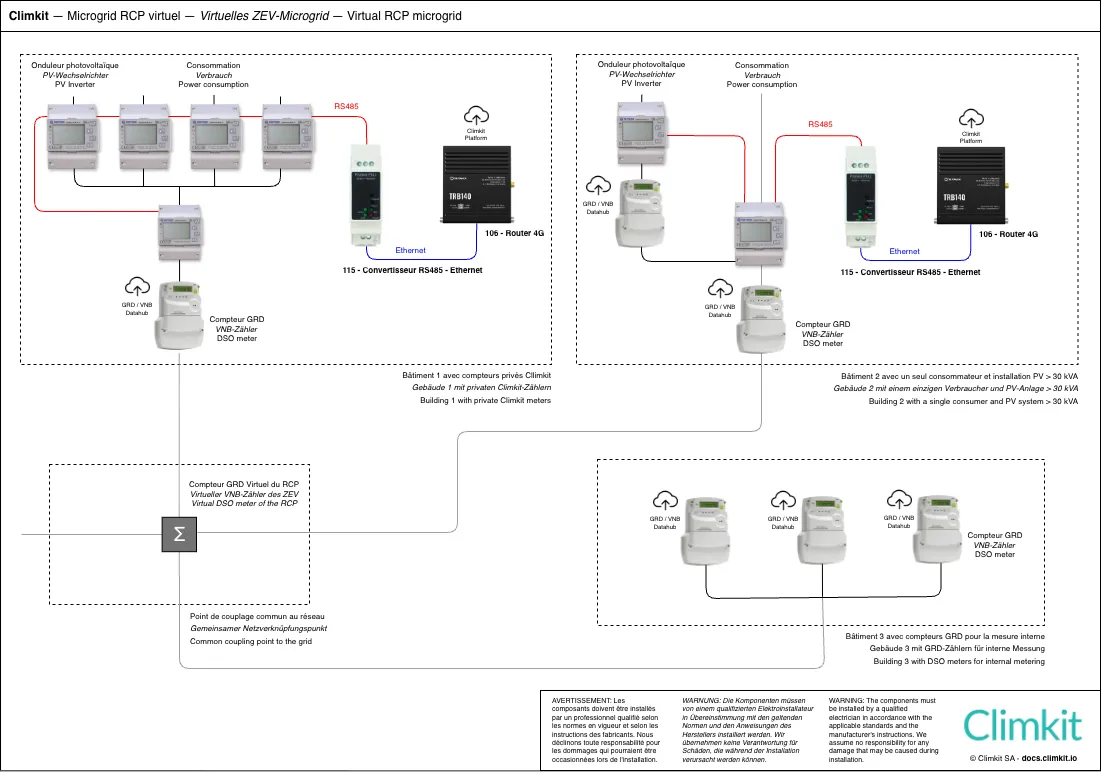
Microgrid diagram: site consisting of several buildings
The Microgrid scheme consists of a grouping (RCP) with the following features:
- A single point of introduction to the public grid, equipped with a DSO input meter, generally located in a separate main switchboard room or in one of the site's buildings.
- Several buildings connected to this same point of introduction.
- Multiple consumers (apartments, offices, common areas, etc.), each linked to an individual meter.
This scheme applies specifically when private meters are distributed across different points of the site. Several variants are then possible for connection and meter reading:
- Installation of a bus between buildings, passing through each meter to the central Climkit Gateway.
- Installation of a Climkit Gateway in each building, each connected to the Internet for data transmission.
- Recommended: Interconnect all buildings via a local IP network (RJ45 or fiber optic cabling). Each meter installation is connected to an RS485-Ethernet converter, which is itself connected to the site's LAN. This architecture allows for efficient data centralization while ensuring infrastructure flexibility. (See diagram below.)
This last variant is recommended as it offers several advantages:
- Increased reliability: It avoids connection problems related to the physical bus between buildings, which can be complex to diagnose and troubleshoot.
- Equipment savings: It allows installing only one Gateway and one router for the entire site, thus simplifying the architecture and reducing costs.
Microgrid diagram with virtual RCP with several introductions
The Microgrid diagram with virtual RCP consists of:
- Several points of introduction to the public grid, each with its DSO meter
- Several interconnected buildings
- Several consumers (apartments, offices, common areas, etc.) equipped with either a private meter or a DSO meter
- Several photovoltaic installations measured by a private meter or a DSO meter
Operating principle:
Produced electricity is shared among the buildings. DSO meters are virtually grouped to establish a single invoice for grid withdrawal.
Private meters are read directly by the Climkit Gateway, while the DSO transmits data from its meters to Climkit. All information is centralized on the Climkit platform.
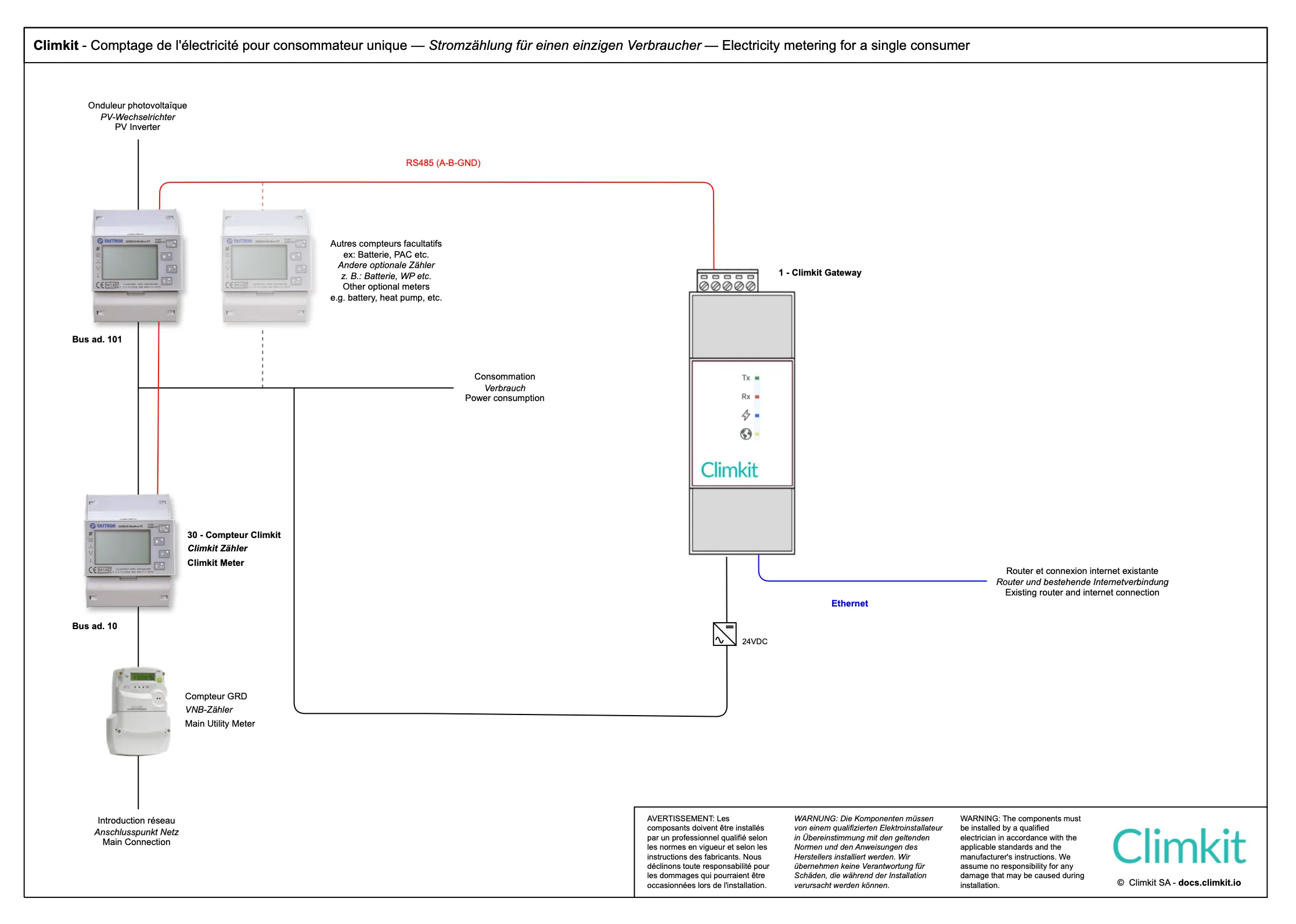
Single consumer diagram
This scheme applies to sites including:
- A single point of introduction to the public grid
- A single consumer
- A single photovoltaic installation
Example application: A detached house or a commercial building equipped with a photovoltaic installation.
At least two meters are installed: an introduction meter in series with the DSO meter and a photovoltaic production meter.
Consumption does not need to be measured directly: it is deduced by calculation from the values of the other two meters (Consumption = Production + Withdrawal or - Injection).
Cloud Gateway variant with LAN router (or 4G)
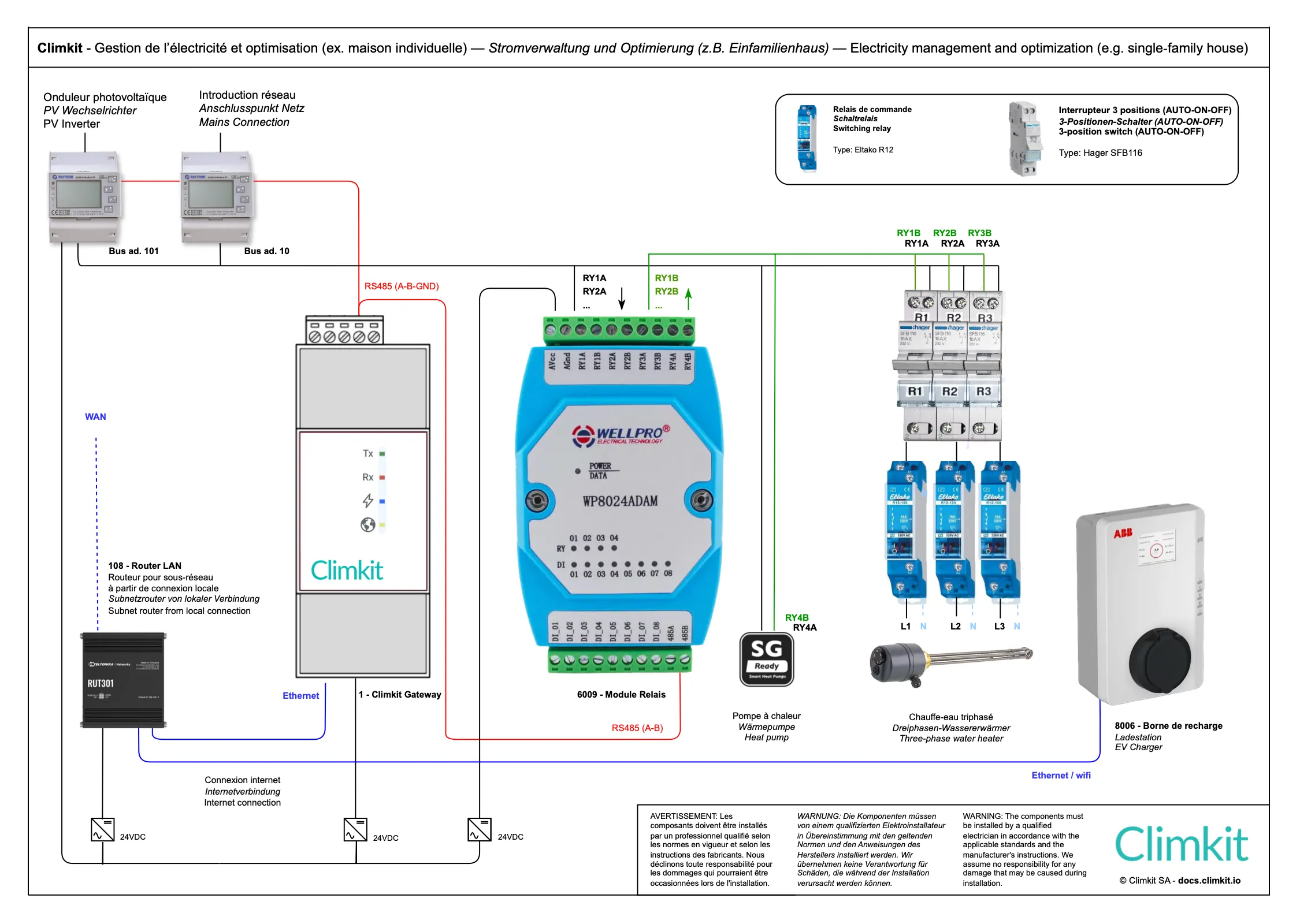
3. Optimization of self-consumption
Climkit's optimization system allows increasing the self-consumption rate of a photovoltaic installation by controlling certain devices based on solar energy production.
The surplus fed back to the electrical grid is thus limited and autonomy is increased by, for example, producing hot water with solar energy.
Devices (water heaters, heat pumps, radiators, pool pumps etc.) are controlled via a relay. It is also possible to control certain charging stations for electric vehicles (via Wifi or Ethernet).
Climkit offer
Here are the additional products to enable self-consumption optimization:
- Equipment:
- Relay I/O Module
- Software features:
- Optimization of self-consumption
- Setup service:
- Technical coordination and configuration
Details of equipment used
Relay I/O Module
The WP8024 I/O Module provided by Climkit has 4 relays.
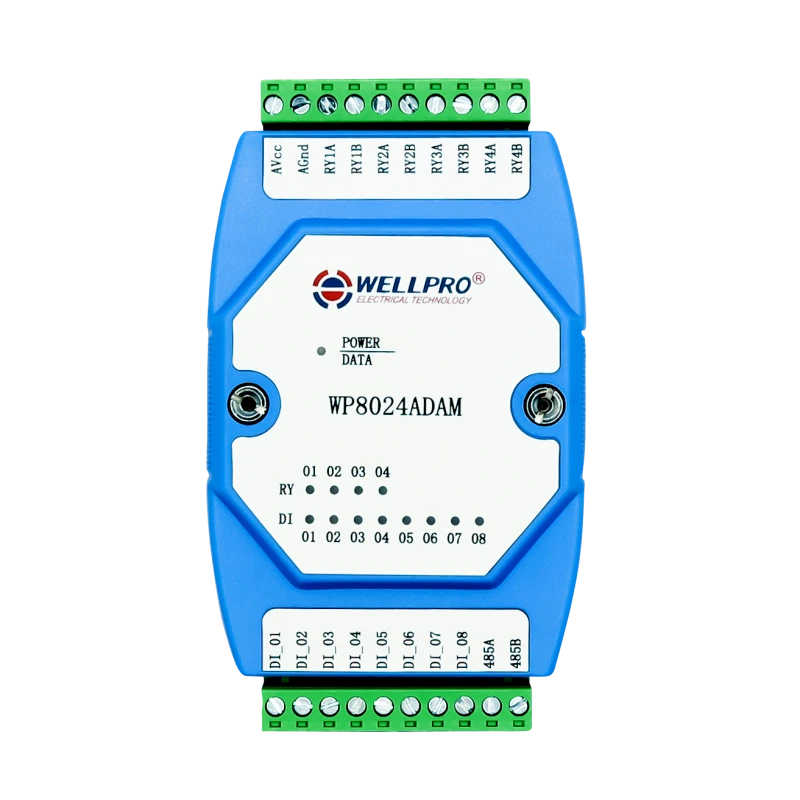

It is delivered with a 24V DC DIN rail power supply and connects to the Climkit Gateway via RS485-Modbus (same as electricity meters).
Potential-free contacts (e.g. Heat pump SG-ready) can be connected directly to a module relay.
In the case of a water heater, the module relays control command relays (contactor) which themselves engage the water heater.
A three-phase water heater resistor can be connected with an independent relay per phase to allow step-by-step engagement and maximize self-consumption even in case of low photovoltaic production.
If 4 relays are not enough, it is possible to connect multiple modules to the Climkit Gateway.
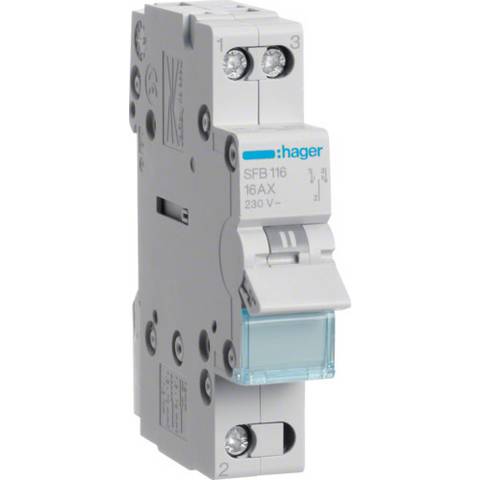
It is recommended to install a 3-position switch between the relay module and the device to be controlled in order to manually engage the latter.
Positions:
- Up (I): Automatic controlled by the relay module and the optimization system
- Middle (0): Forced stop
- Down (II): Forced run
Typical model: Hager SFB116

4. Battery installation
In the case of an installation with an AC-type battery (equipped with its own charger-inverter), it is essential to connect this system to a specific Climkit battery meter and configure the latter in "Battery" mode on the platform.
