Table of Contents
Global planning of a Climkit site
The Climkit energy management system covers various needs related to the management of energy flows on a site. Depending on the building configuration and the intended uses, a project can concern a single energy flow or combine several.
This article presents all the solutions offered by Climkit as well as the main technical installation options associated. It serves as support for project planning to quickly identify relevant elements and structure the installation consistently.
Solutions can be deployed independently or combined according to the site's needs. This flexibility allows the installation to be adapted without unnecessary complexity.
Climkit solutions
A Climkit solution corresponds to the setup of all elements necessary for managing a given energy flow on a site.
It combines hardware equipment, software features, and commissioning services, supplemented where necessary by operational services.
Each solution allows for measuring and controlling consumption, ensuring fair allocation and individual billing between different occupants and consumers.
For each solution, a list of preliminary questions serves as support for technical reflection and allows anticipating points to be clarified during project preparation.
In case of doubt about the configuration to be adopted or compatibility with an existing site, an early exchange with Climkit allows for the validation of a principle diagram and helps avoid subsequent adjustments.
Communication with the Climkit Gateway
All Climkit solutions require the Gateway to communicate with the various equipment installed, notably meters and charging stations.


Preliminary questions
- Is a wired Internet connection available on-site or should a Climkit 4G Router be planned?
- Is there a 4G signal in the electrical room or should an extension and/or external antenna be planned?
- Are there several buildings on the site and several electrical rooms? Can they be connected by a bus or Ethernet cable?
Electricity management and RCP
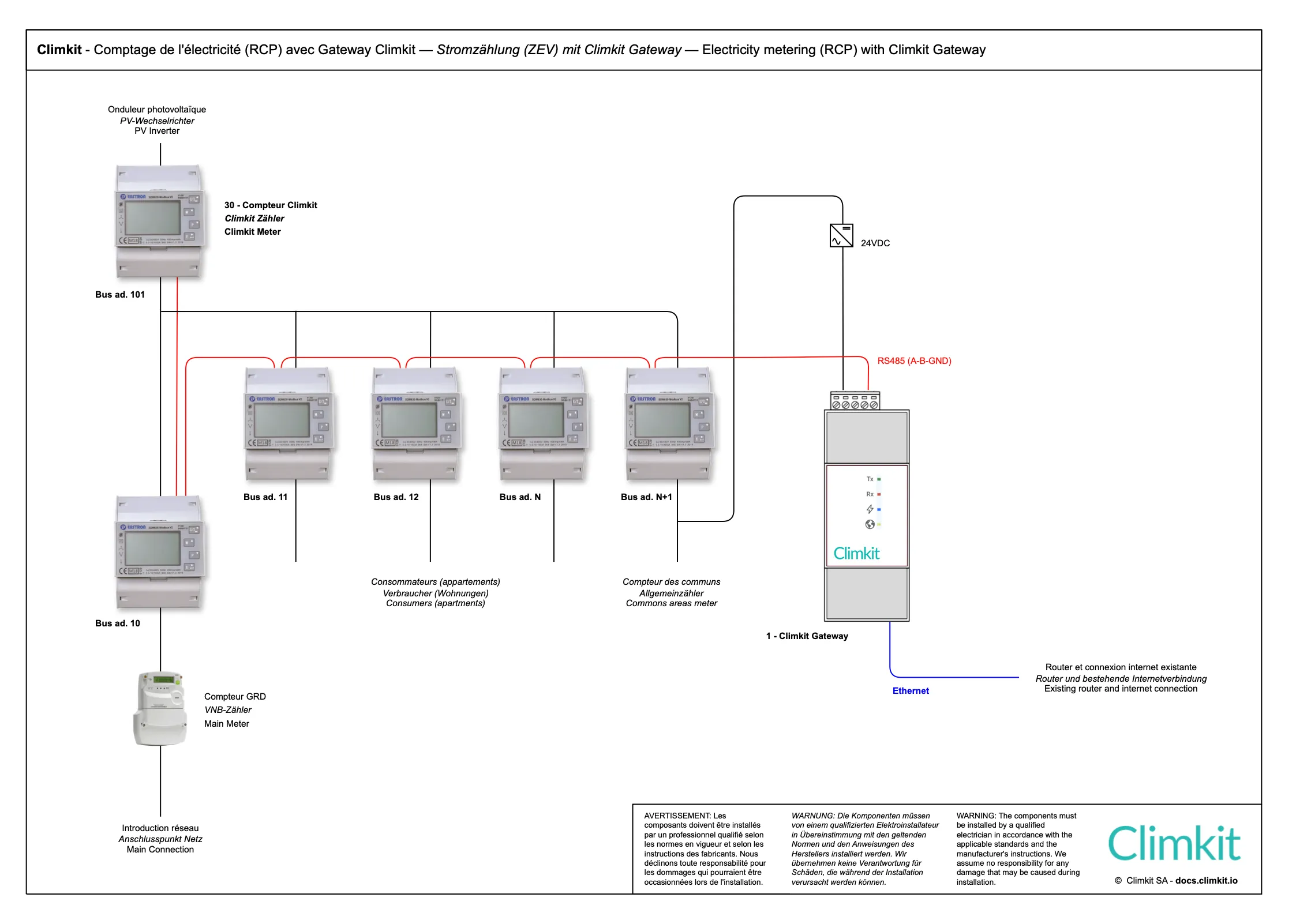
In a building equipped with a Photovoltaic installation and structured as a Self-consumption community (RCP), Climkit provides complete management of the electricity produced and consumed by linking the various meters to a Climkit gateway to measure, distribute, and visualize energy flows.
This approach allows for optimized collective self-consumption, while ensuring fair billing of the energy used. Each resident can track their consumption in real-time on the platform.
The principle is based on private electricity meters connected to the Gateway via an RS485 communication bus and the open Modbus protocol:
Optimization of self-consumption
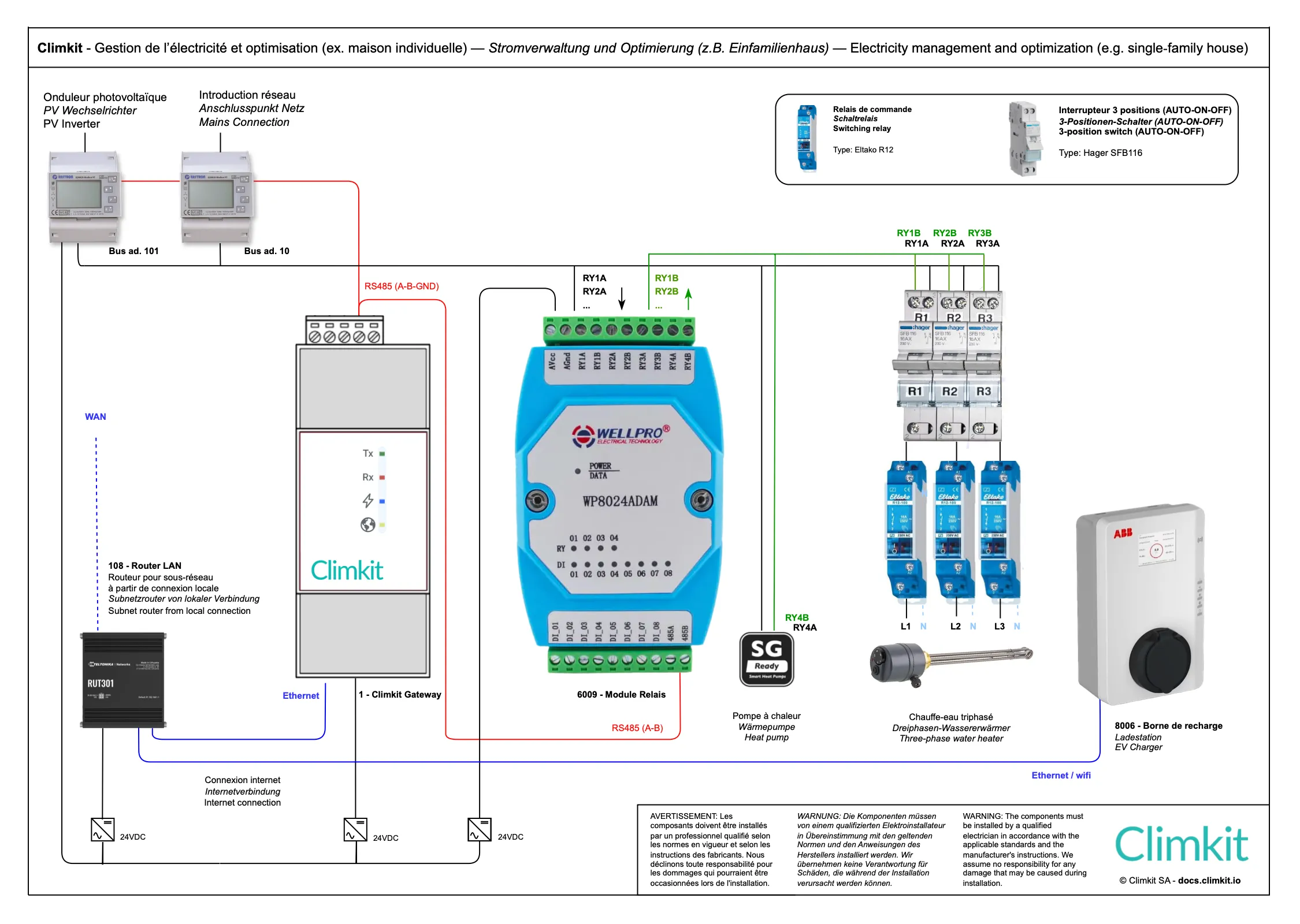
When appliances like water heaters, heat pumps, or charging stations use locally produced photovoltaic energy, Climkit's Optimization option increases the self-consumption rate by controlling certain appliances based on surplus solar energy production.
Installation examples
Site in RCP including private meters for apartments, common areas, photovoltaic production, and general network input in series with the DSO input meter.
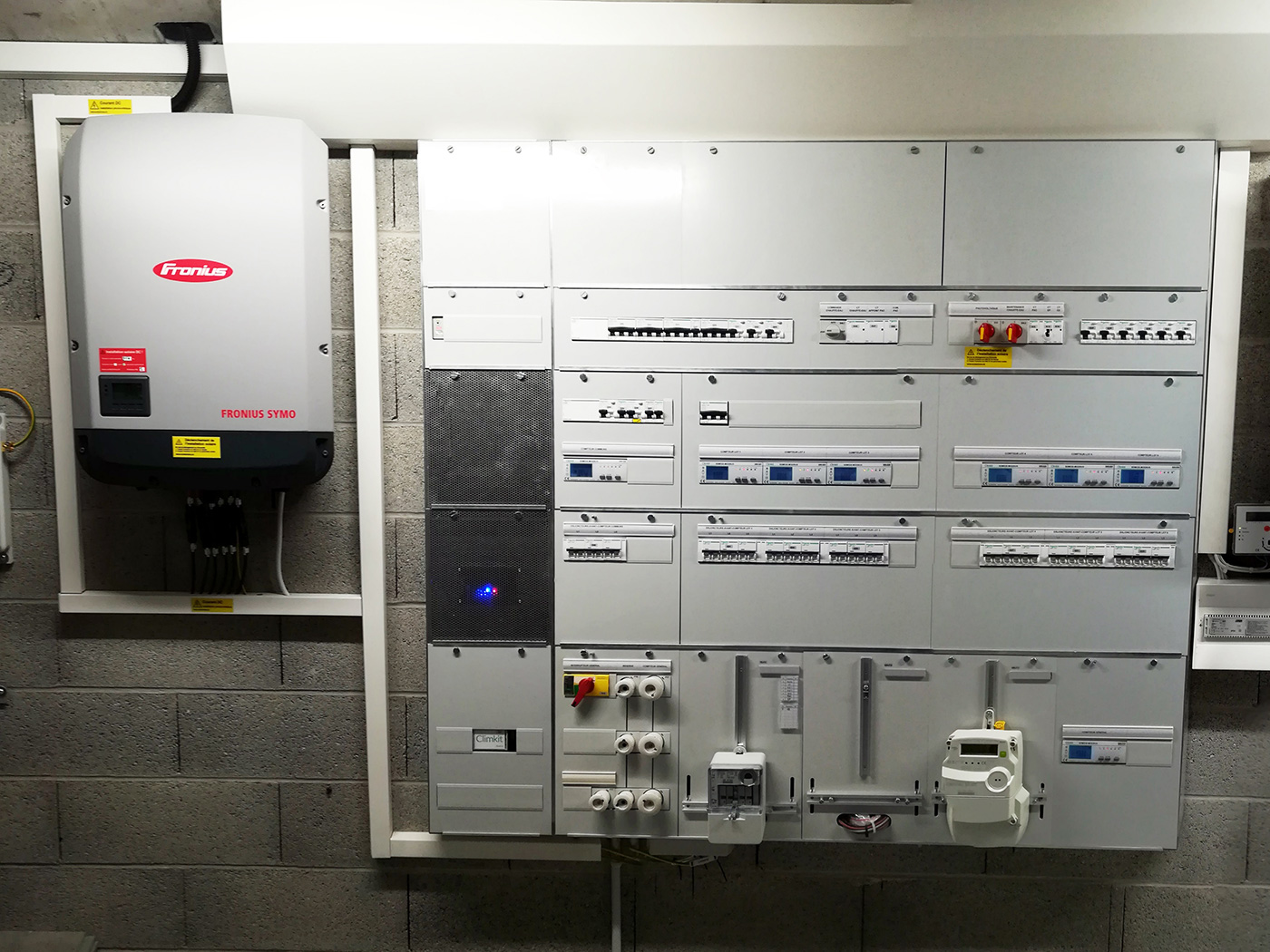

Site in RCP with a distribution board and its private meters for apartments and common areas and an input board with private Climkit meters and DSO meters for input and photovoltaic production:
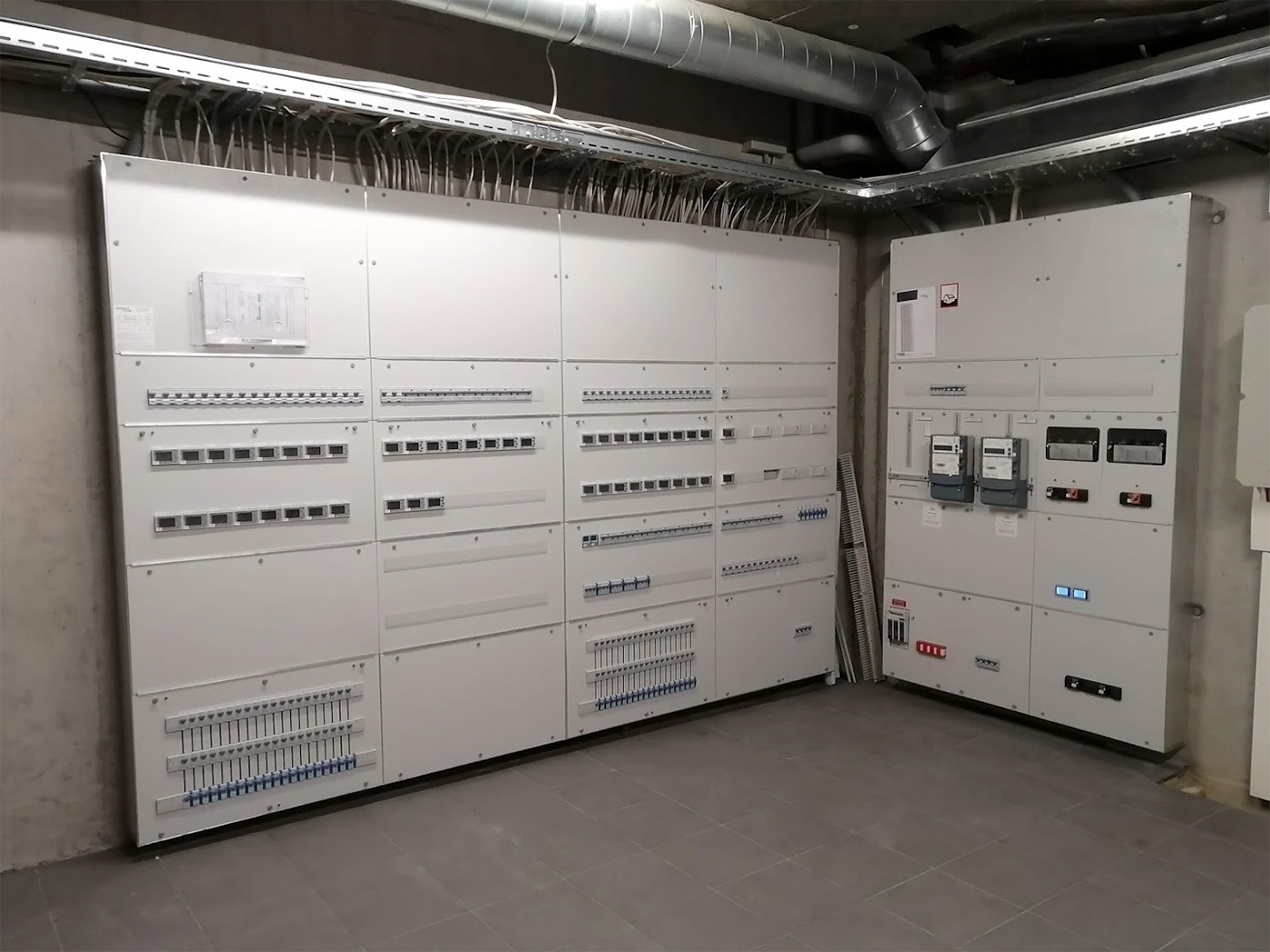

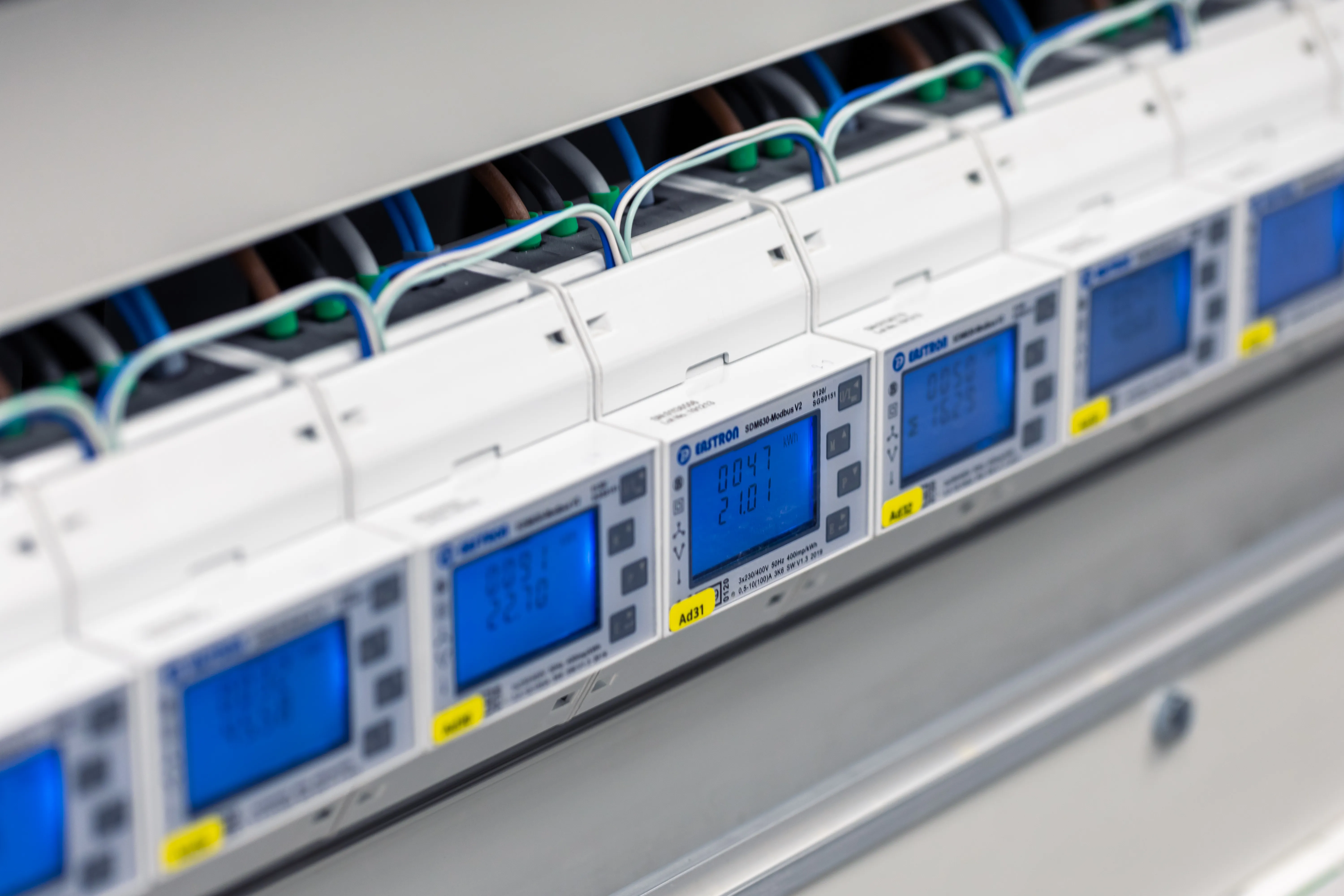
The meters are connected in series to the Climkit Gateway by an RS485 communication bus.

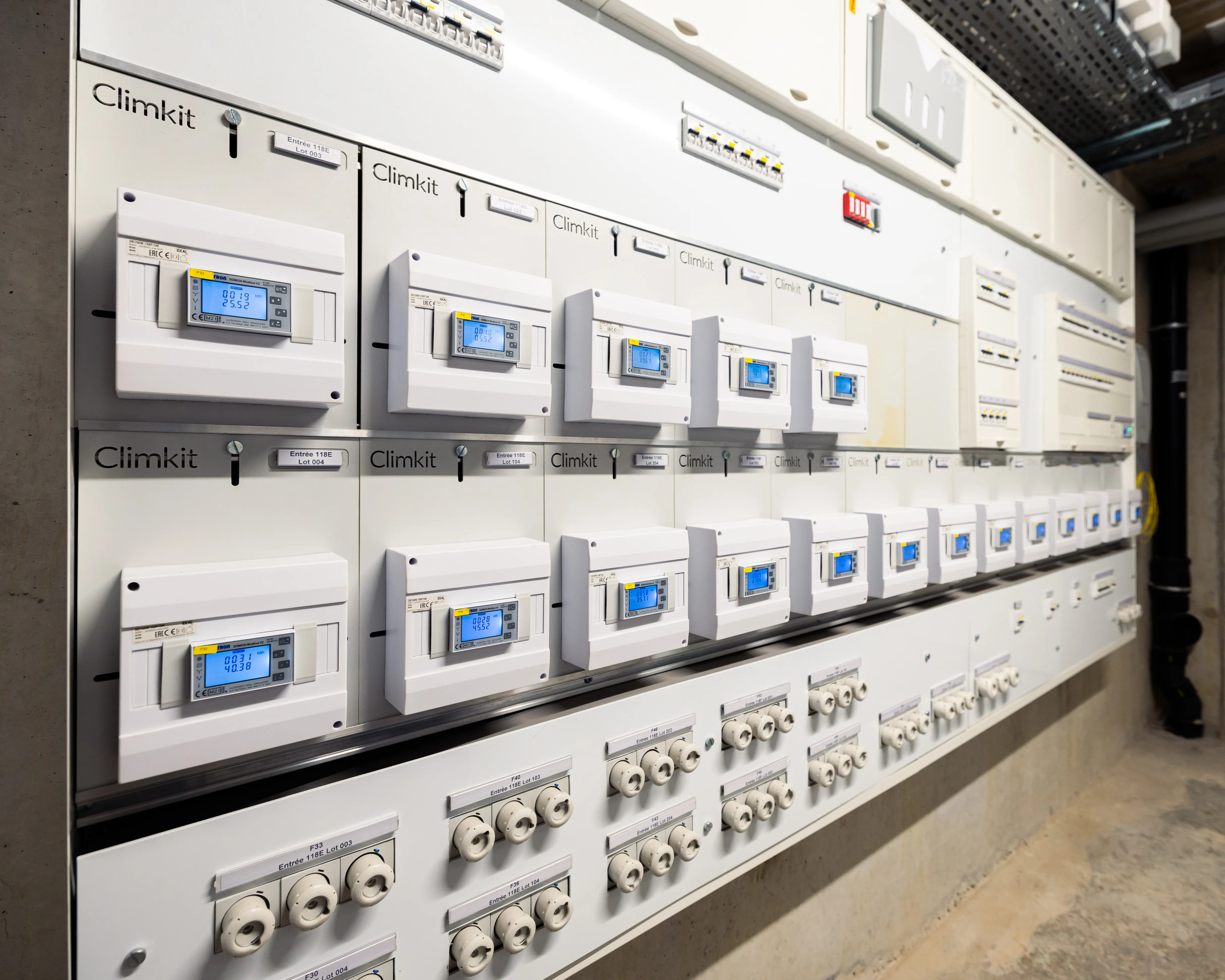
Board with installation of Climkit meters on existing DSO meter locations thanks to the Climkit T-Box kit (plate and DIN box):

Preliminary questions
- Is it planned to manage electricity, for example within an RCP?
- What is the number and type of meters to be planned?
- General input to the electrical grid
- Photovoltaic installation(s)
- Housing / apartments
- Annex premises, businesses
- Common areas
- Other common areas like the parking lot
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Battery
- Other surfaces
- Which meters are direct (<80A)?
- Which meters are indirect with CTs? What amperage for the CTs?
- Are the meters integrated into the electrical board or is it planned to install them on existing DSO meter locations?
- Is it planned to install a storage system (battery)?
- Can we plan for self-consumption optimization by controlling the heat pump or water heater?
Management of electric vehicle charging stations
Climkit allows for the installation and management of charging stations in collective parking lots.
The system regulates the charging power based on grid capacity and available energy, controls access via individual RFID badges, and manages the billing of charges for each consumer.
The stations communicate with the Gateway via Wi-Fi or Ethernet using the OCPP protocol:
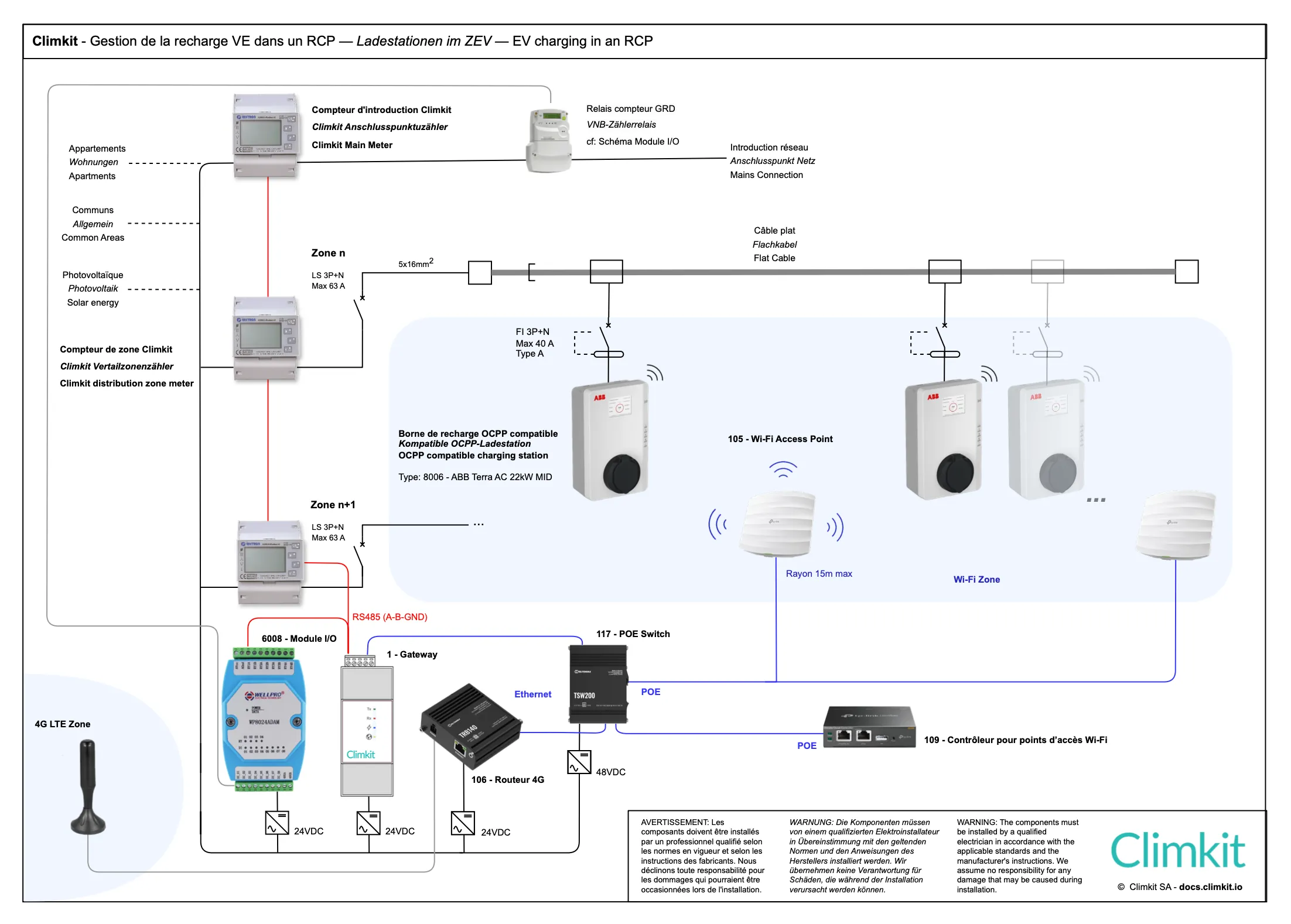
Flat cable and Wi-Fi
Climkit recommends a basic infrastructure consisting of a flat cable and a Wi-Fi network to facilitate the progressive addition of stations without heavy intervention on the existing wiring.
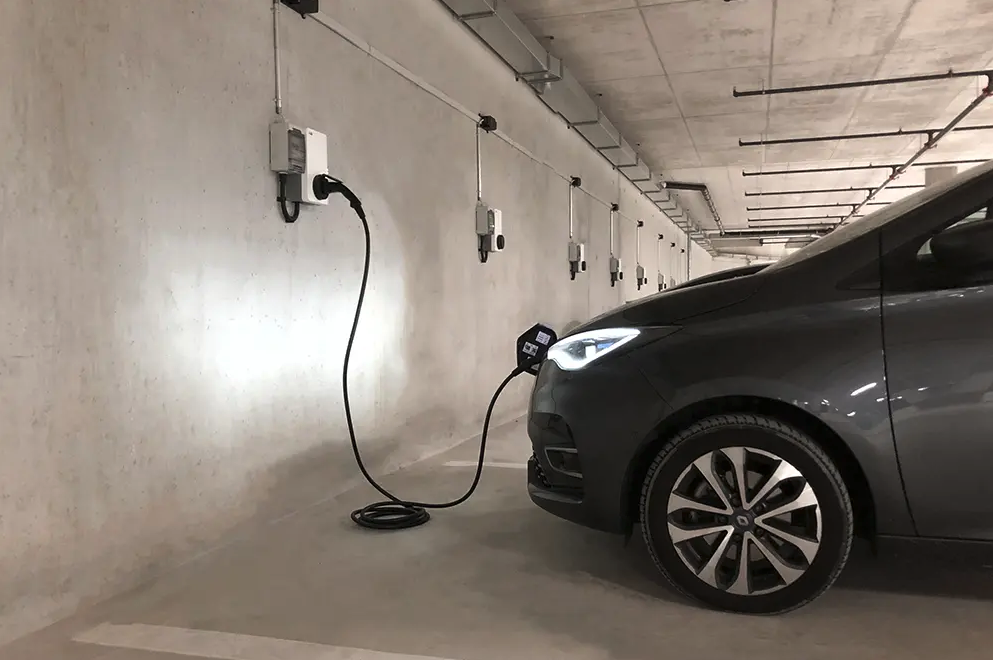
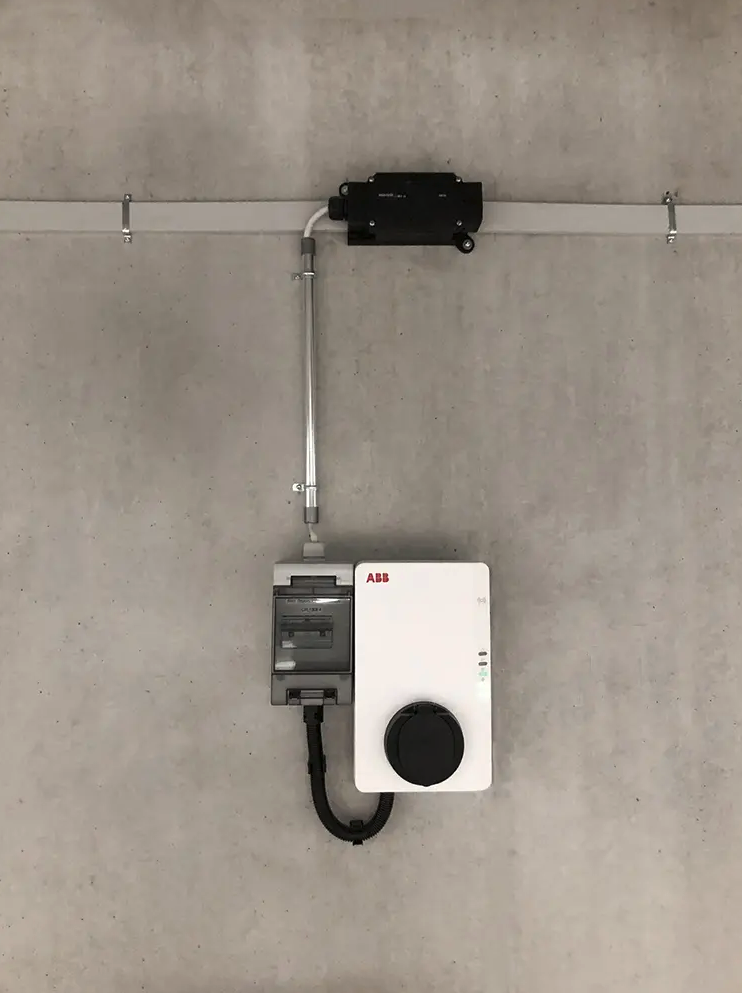


Preliminary questions
- Is it a scalable installation with flat cable or only a few stations?
- How many spaces could accommodate a charging station?
- How many flat cable departures are planned in the electrical board?
- How many stations should be planned immediately?
- Do the stations communicate via Wi-Fi or are they connected to the IP network via wired Ethernet/RJ45?
Management of thermal energy and water
Climkit provides the reading of heating and hot water consumption in accordance with the requirements of the federal regulation on individual statements of energy and water costs (DIFEE).
Each dwelling or surface is equipped with a heat meter (heating) and a hot water meter, supplemented by general meters allowing for the distribution of the share of common areas and that of hot water production.
These measurements are used to establish transparent and accurate statements, based on actual consumption rather than estimates or based on surface area.
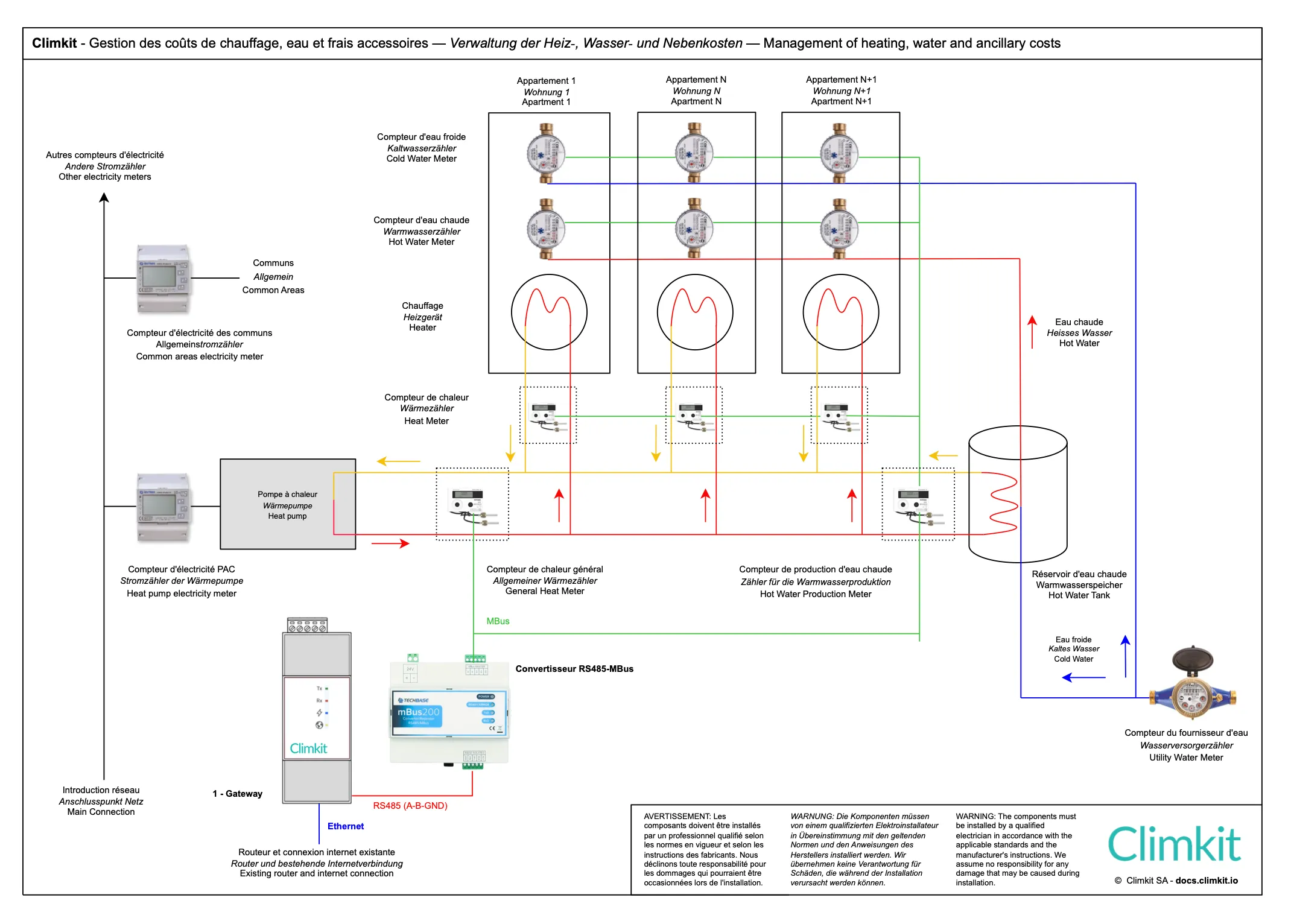
Example of a heat collector located in an individual apartment and equipped with a heat meter:
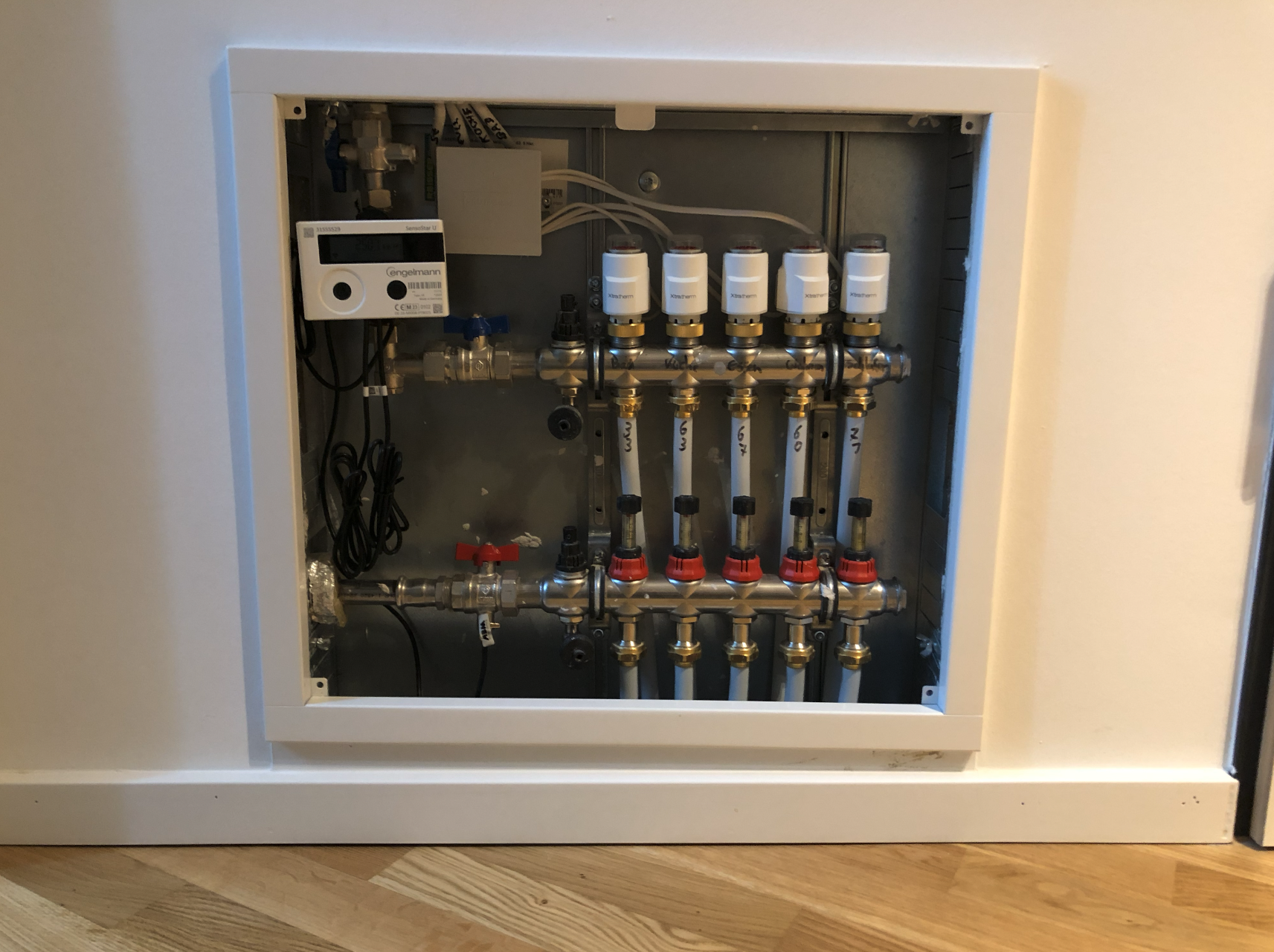

Preliminary questions
- Is it planned to install wired M-Bus type heating and water meters?
- What types and how many meters are planned: hot water, cold water, heat?
- Is the meter bus brought back to a single location near the electrical board?
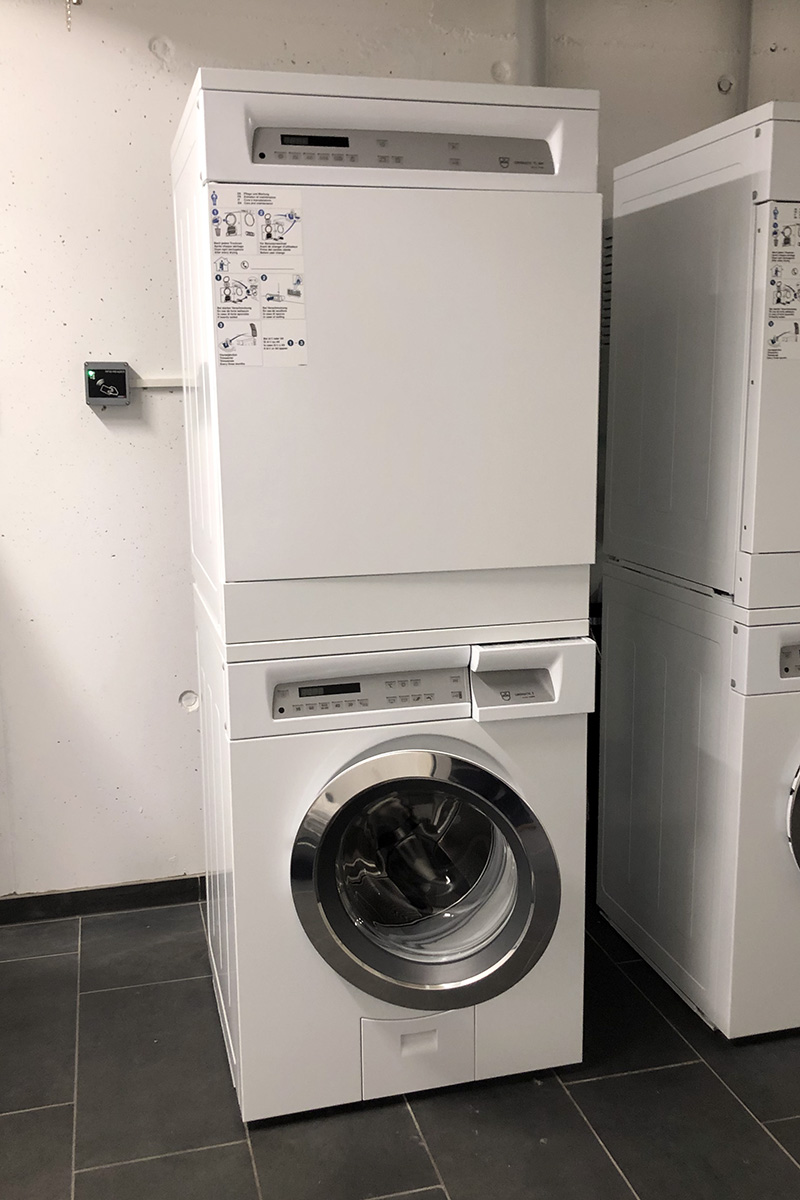
Management of collective laundries
Climkit offers a simple and reliable system for managing common laundry rooms.
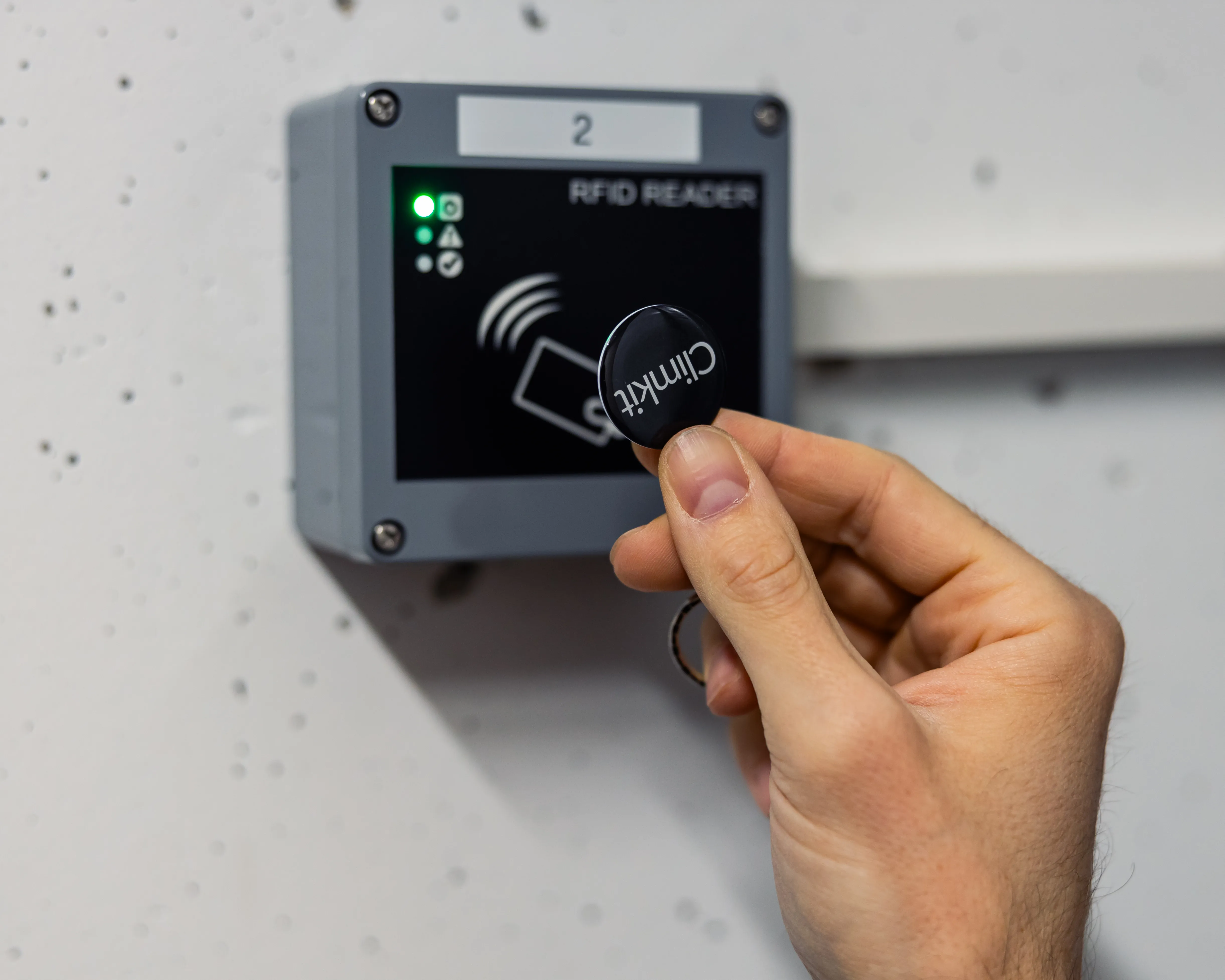
An RFID reader connected to the Gateway identifies users and switches on the power supply to washing machines, tumble dryers, or secomats.
This system integrates naturally with other Climkit solutions, allowing all consumption to be grouped on the same platform.
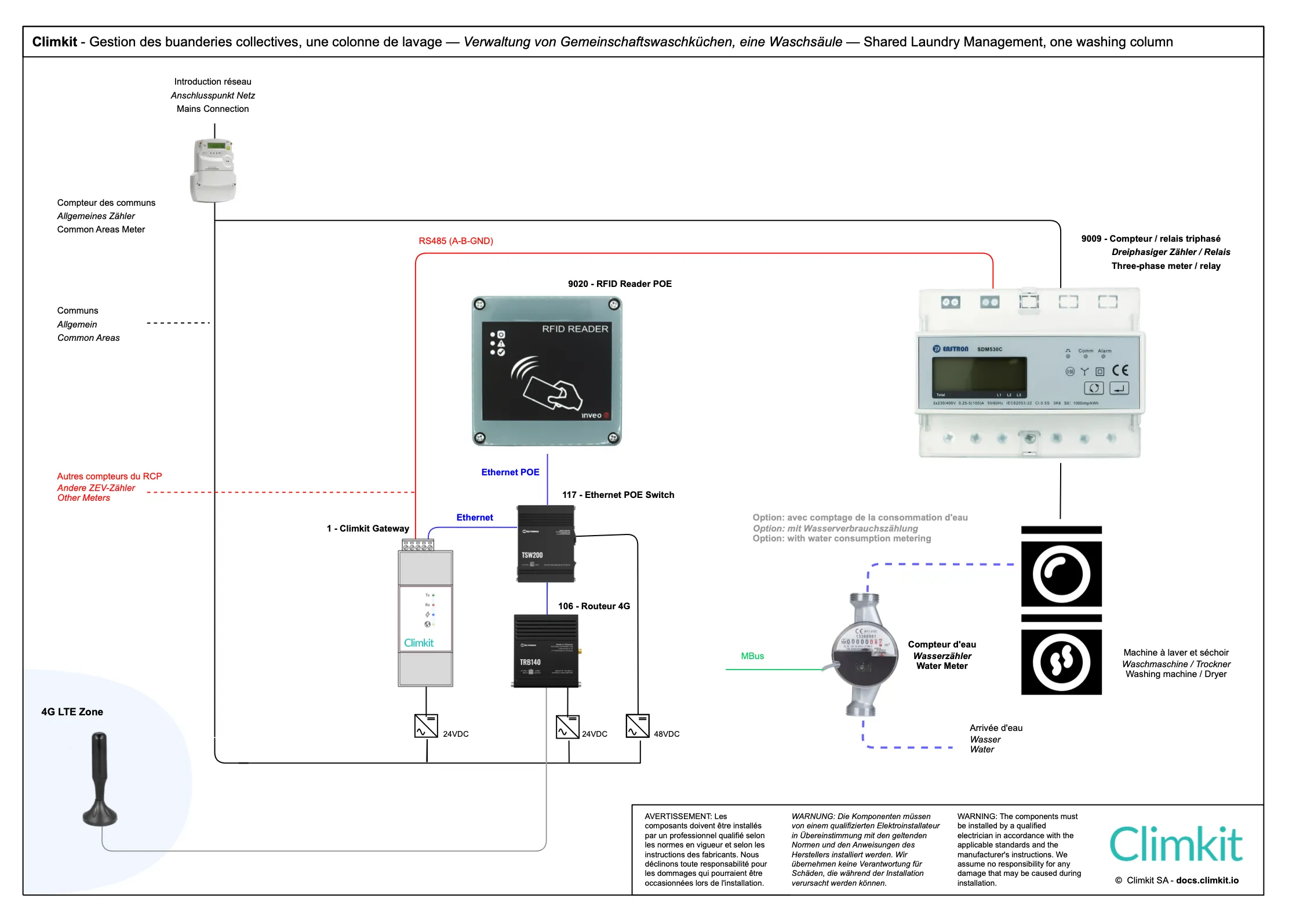
Washing column with RFID reader fixed to the wall on the left

RFID without keypad for a single washing column

Preliminary questions
- How many laundry rooms are there?
- How many washing machines, tumble dryers, and secomats per laundry room?
Management of electric bike charging
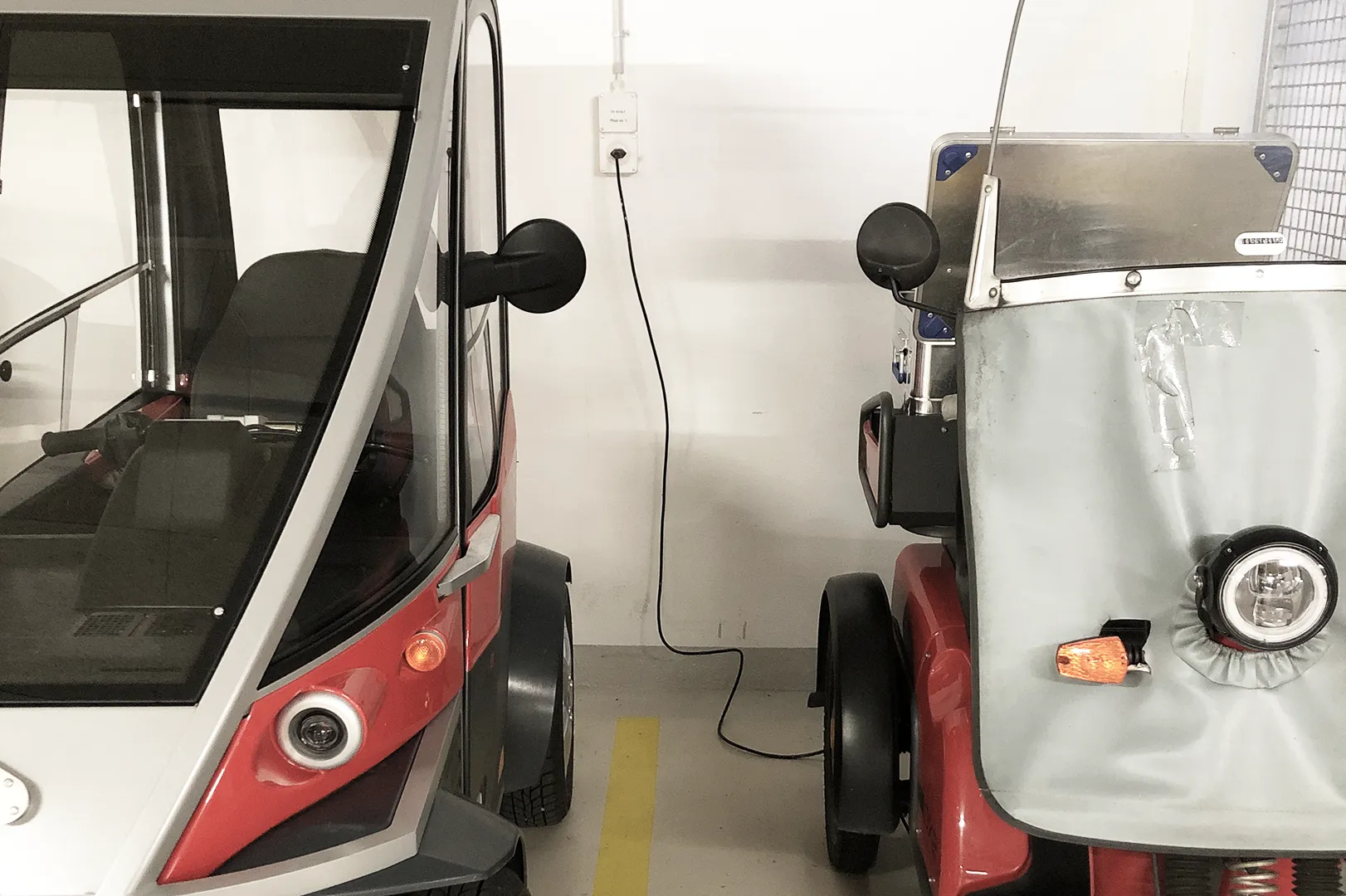
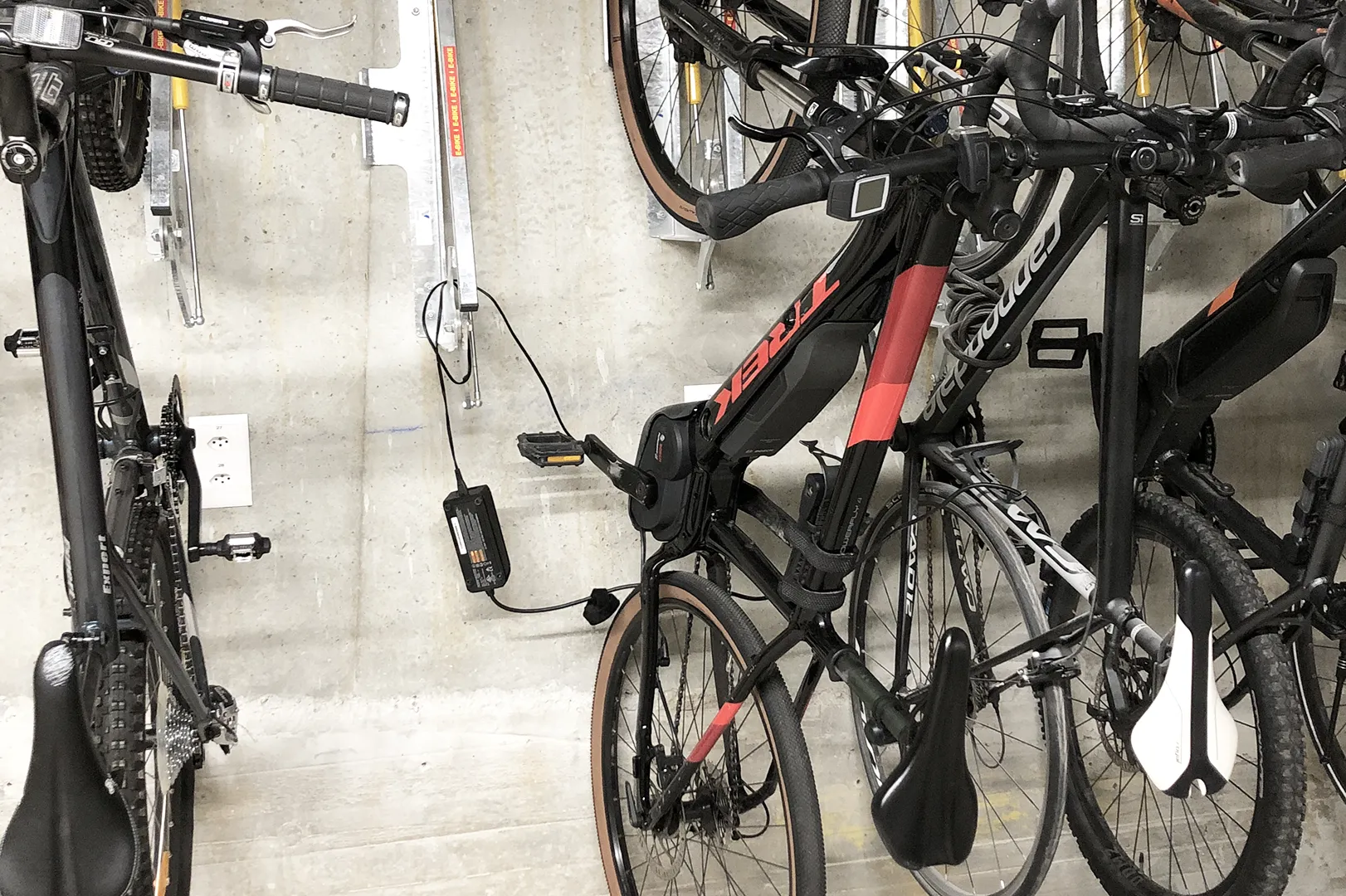
Climkit allows for the installation of connected outlets that offer residents the ability to charge their electric bikes or scooters.
Access is via RFID badge and consumption is recorded individually.
Here is a typical connection diagram:
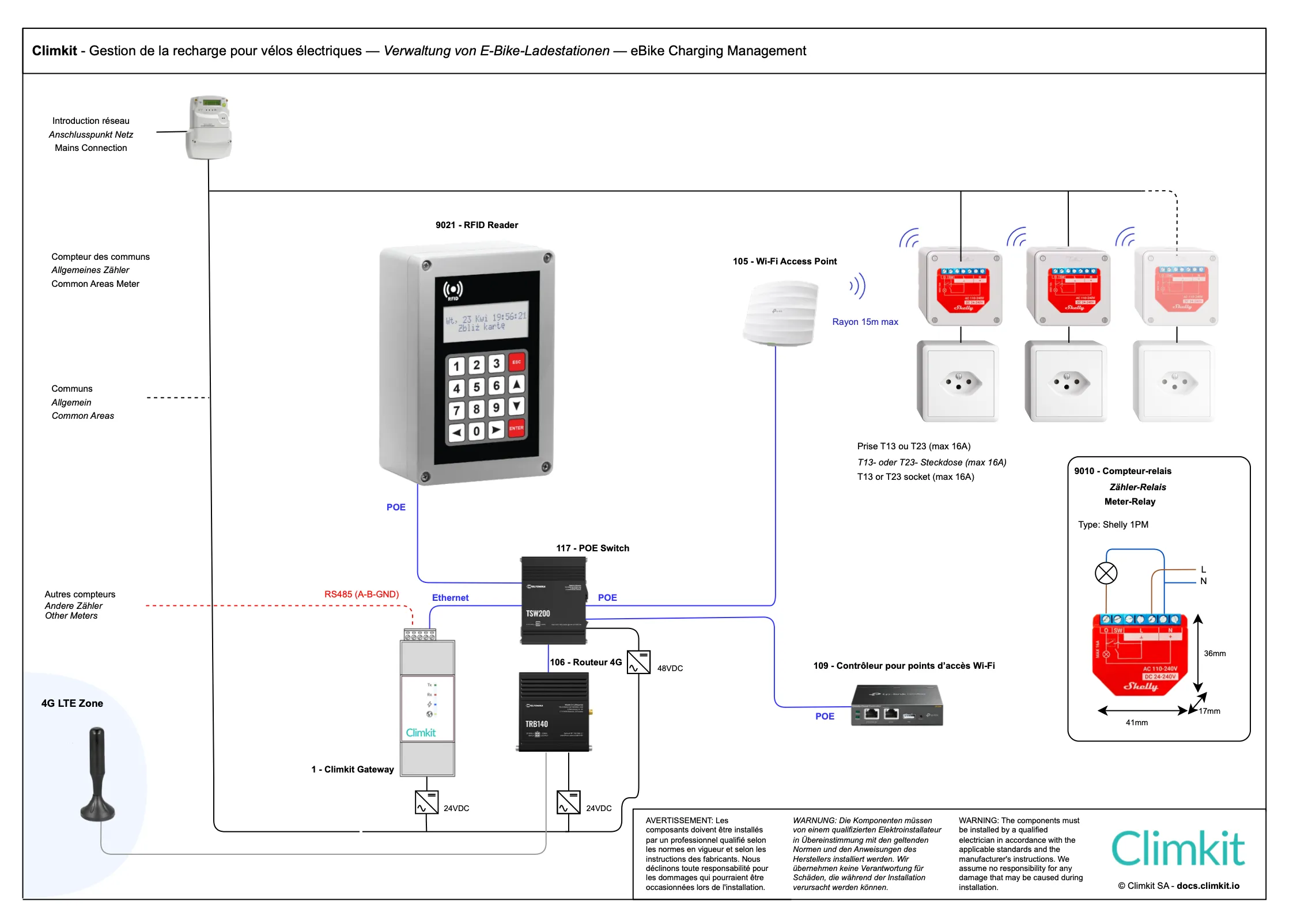
Installations with surface-mounted or integrated outlets:



Preliminary questions
- How many bike rooms need to be equipped?
- Is the bike room inside or outside?
- What is the number of outlets?
