Virtual assistant
Installer
Getting Started Guide
Solutions and documentation structure
Equipment ordering and commissioning
General terms and conditions of sale and warranty
Wiring diagrams
Gateway and communication
Community - Electricity Metering - RCP
Heating - Heating metering and water
Mobility - EV Charging Stations
EBike - Recharge electric bikes
Washaccess - Collective laundry manager
Self-consumption optimization
Building energy monitoring
Equipment and installation
Charging infrastructure and relays
Metering infrastructure
Communication infrastructure
Climkit Gateway
4G Router
LAN Router
RS485-Ethernet Converter
Switch ethernet DIN POE
WiFi Network
MBus-RS485 Converter
Storage system (battery)
Configuration and commissioning
Commissioning
Getting Started Guide
Add a router to a site
Add a Climkit Gateway to a site
Electricity meter configuration
Charging station configuration
Configuration of heating and water meters (MBus)
Installation of Shelly relay meters
Optimization via EV relays and charging stations
Checking meter connection status
Advanced configuration
Configuration Gateway
RFID reader and relay meter configuration
IP network configuration and routers
RS485-Ethernet TCP/IP Converters
Configure Teltonika RUT241
Display configuration
Modbus Meter Configuration
Metering data processing
Manually read meter
Inepro PRO380 Meters and various
ABB Terra AC Charging Station Configuration
Wallbox configuration
Firewall rules for Climkit Gateway
Schneider EVlink Pro AC Charging Station Configuration
Zaptec Charging Station Configuration
Owner
Administrative setup
Getting started guide - administrative setup
Form - 1. Contact details
Form - 2. Solutions
Form - 3. Rates
Contract and documents to complete
Owner account
Consumer information flyers
Online access, RFID badge and charging stations
FAQ and other information
Resident
Platform
Platform access
Terminology
Site
Parameters
Creation/edit of a note or to-do item
Closing an open issue
Site statuses
Add/Modify building(s)
The steps for setting up a site
Delete/deactivate a site
Add/Edit Equipment(s)
Modify site basic information
Equipment
Add/modify a gateway
Add/modify a router
Add/modify an electricity meter
Bulk meter insertion
Mass assigning meters to a gateway
Add/edit a distribution zone
Add/modify a charging station
Add/modify a thermal or water meter
Add/edit a DSO meter (FTP transfer)
Remote connection to a Climkit gateway
Administration
Stakeholders
Financial conditions
Visualizing Site Management Conditions
Activating/Deactivating a Solution
Configuration of the Operating Method
Visualizing Financial Conditions
Creation/editing/addition of a financial condition
Removal of a financial condition
Accounts
Create a consumer account
Create a contact
View and download account invoices
Send platform access to a contact
Add/modify billing address
Link an existing account to a site
Changing the correspondence method
Rates and billing points
Creating/editing a billing point
Register a move (relocation)
Account assignment to a billing point
Add/edit default charge advance payment for a billing point
View site consumption rates
Consumption Rate Edition
Creation/editing of a consumption tariff
Creation/editing of a Tariff component
View fixed rates and subscriptions
Customize invoice position labels/titles
View Financial conditions billed at billing points
RFID badges
Accounting
Tools
Meter control
Visualization
Expense accounts
Introduction to the Expense Statement Tool
Create/edit an expense accounting period
Modify expense statement settings
Add/edit a overhead expense invoice on an expense statement
Edit collected advance payments of an expense statement
Specifics of heating and hot water production costs
Check and download meter readings for the cost accounting period
Allocate expenses and generate expense statements
Exporting individual consumptions for the billing period
API
- Categories
- Installer
- Equipment and installation
- Storage system (battery)
Storage system (battery)
Installing a battery allows for the storage of surplus Photovoltaic (PV) electricity produced on a site. When PV production exceeds instantaneous consumption, the surplus is stored in the battery.
Once the battery is fully charged, any further surplus is fed into the electrical grid.
When consumption exceeds solar production alone, the battery discharges to power the building's consumers. This mechanism significantly increases the self-consumption rate, as solar electricity produced during the day is also available at night.
When the battery is depleted, the remaining electricity deficit is automatically drawn from the grid.
Each battery system is equipped with a Battery Management System (BMS) that continuously supervises inbound and outbound energy flows.
Thanks to a sensor installed at the building's electrical input, the BMS intelligently regulates charging and discharging: in the event of solar surplus ready to be injected into the grid, it triggers the battery charge to store this surplus; conversely, when a demand for electricity from the grid is detected, it prioritizes battery discharge to reduce grid import volume.
There are two main types of battery systems that can be coupled with a photovoltaic installation:
- Off-grid storage system (AC Battery)
- Hybrid PV Inverter (DC Battery)
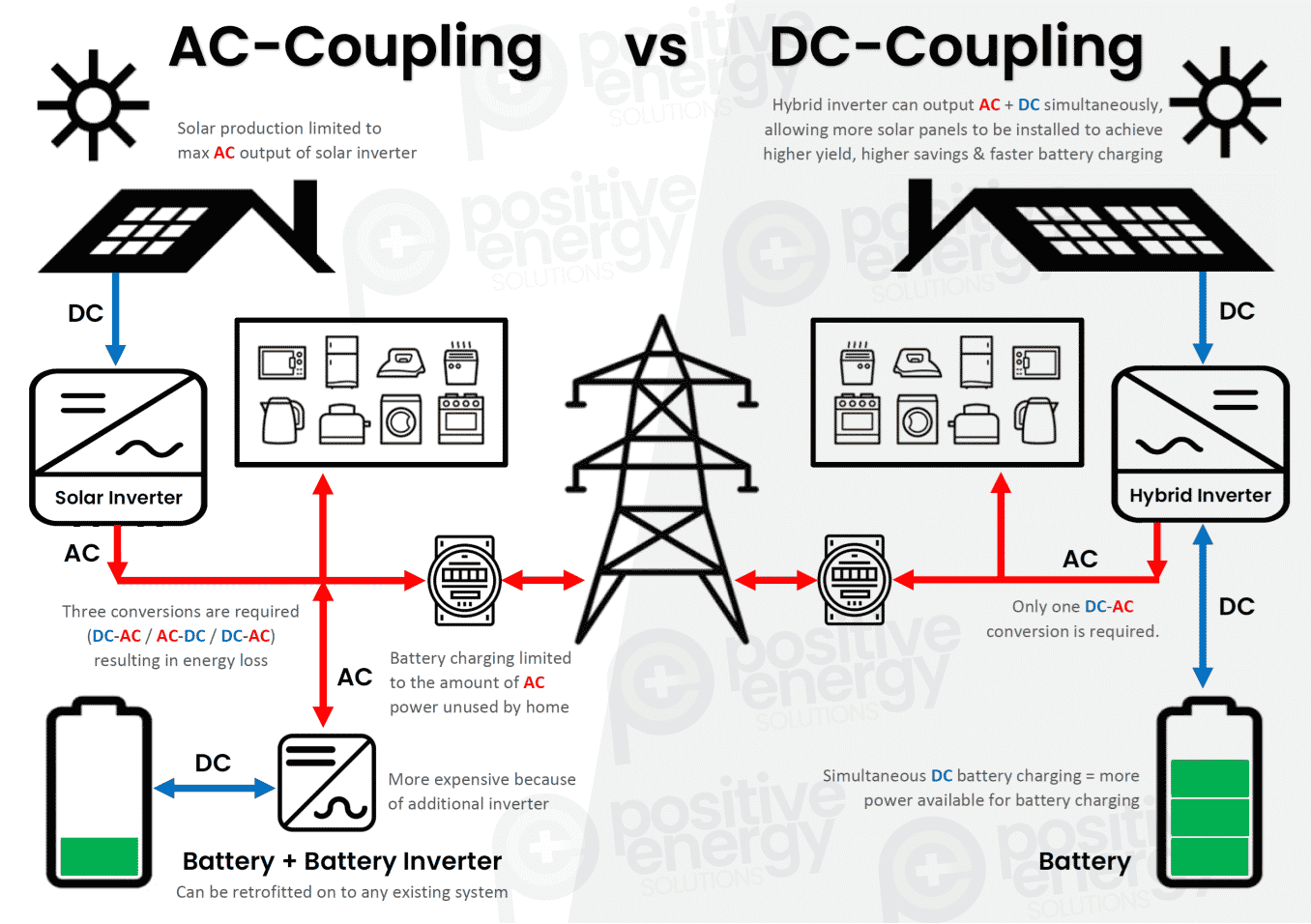
Off-grid storage system (AC Battery)
An AC battery operates with its own inverter-charger, which handles both DC conversion during charging and AC conversion during discharging.
The use of an AC battery requires its connection behind a specific Climkit battery meter, configured in Battery mode on the Platform. This allows the charge and discharge flows to be recorded and visualized directly on the Platform.
One of the main advantages of the AC battery is its independence from the existing photovoltaic installation. It can be easily added to a site already equipped with solar panels, without requiring the replacement or modification of the existing PV inverter.
Hybrid PV Inverter (DC Battery)
A hybrid photovoltaic inverter integrates inverter, management, and battery charging functions. The battery connected to this type of inverter is referred to as a DC battery because it is recharged directly using DC power produced by the PV panels, avoiding double conversion.
The main advantage of a DC/hybrid inverter system is its higher efficiency, as it avoids double conversion (AC→DC→AC) and the associated losses.
However, with this configuration, it is not possible to install a dedicated battery meter because the hybrid inverter and the battery are placed directly behind the PV production meter. Consequently, it is no longer possible to display solar production and battery charge/discharge flows separately.
Generally, hybrid inverters are primarily installed on small-scale photovoltaic installations, typically under 15 kWp, such as those in single-family homes.
Back-up power function
Most photovoltaic inverters do not operate during a grid outage.
However, some hybrid inverters feature a back-up power function, which allows critical building loads (e.g., common area lighting) to remain powered during a grid outage using the energy stored in the battery.
Some models can also automatically trigger a thermal generator to take over during prolonged interruptions.
